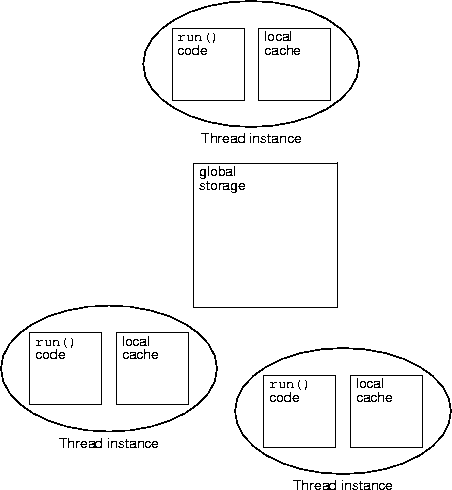

void f(Object obj) int i i = ...
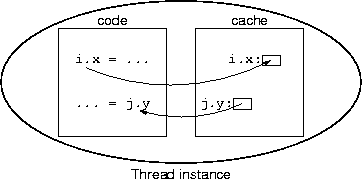
|
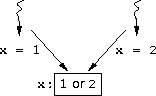
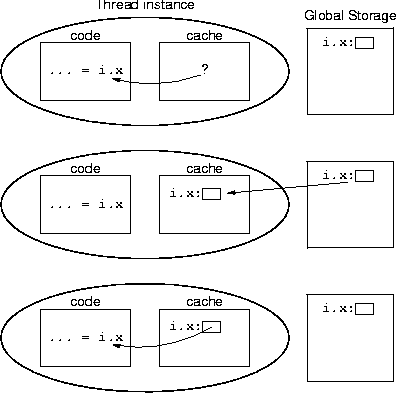
|
long and double are read-write atomic.
long and double need not be read-write atomic.
volatile longs and doubles are read-write atomic.
synchronize also indicates low-level storage updates.
i = j = 0?
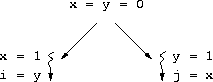
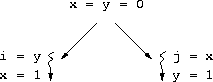
volatile keyword is not transitive.
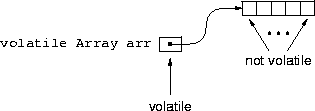
Volatile vs. synchronized
// Using volatile
class Count { volatile int count = 0; }
public void f(Count c) { c.count }
// Using synchronized
class Count { int count = 0; }
public void f(Count c)
synchronized(c) { c.count }
void good_add1(Count c)
synchronized(c) { c.count++ }
void bad_add1(Count c)
c.count++
long and double may not be atomic; other base types are.
This page last modified on 3 July 2003.