global etype a[a_size]
procedure find_seq_max()
returns etype max
int i = lb(a) + 1
max = a[i - 1]
while (i <= ub(a))
if (a[i] > max)
max = a[i]
i++
global etype a[a_size];
procedure find_half_max(int start)
returns etype max
max = a[start]
int i = start + 2;
while (i <= ub(a))
if (a[i] > max)
max = a[i]
i += 2
procedure find_par_max()
returns etype mx
etype odd_max, even_max
co
odd_max = find_half_max(lb(a))
||
even_max = find_half_max(lb(a) + 1)
oc
mx = max(odd_max, even_max)
procedure time_par(int iters) {
# Time the parallel array max.
int stime = age()
for [i = 1 to iters] {
}
const int otime = (age() - stime);
stime = age()
for [i = 1 to iters] {
find_par_max();
}
const int etime = (age() - stime) - otime;
printf("parallel %d elements %4.1f ms/call.\n",
a_size, real(etime)/real(iters))
}

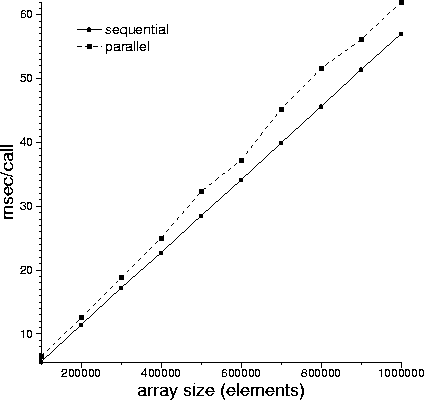
MPD_PARALLEL=1
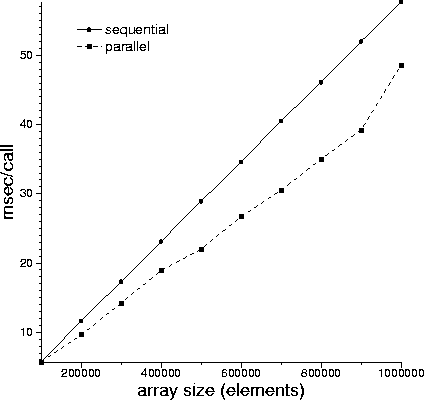
MPD_PARALLEL=2
double a[1:a_size]
double a_max
sem mutex = 1
procedure find_global_half_max(int start)
int i = start;
while (i <= ub(a))
P(mutex)
if (a[i] > a_max)
a_max = a[i]
V(mutex)
i += 2
procedure find_seqpar_max()
const int i = lb(a)
a_max = a[i]
co
find_global_half_max(i)
||
find_global_half_max(i + 1)
oc
See the complete code.
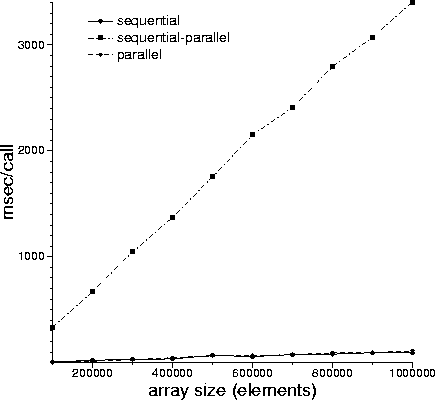
MPD_PARALLEL=1
MPD_PARALLEL=2 coredumps. A lot.
This page last modified on 7 July 2002.