Operating Systems Lecture Notes
21 March 2012 • File-Systems Background
Outline
|
|
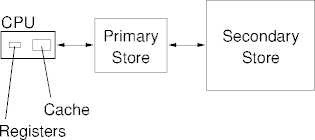
The Story So Far
- Small, fast, expensive on the left.
- Large, slow, cheap on the right.
A New Dimension Enters
- Storage is persistent if written data stays written.
- Data are represented as large-scale physical change.
- Magnetic alignment, optical polarization.
- Persistent storage tends quickly to the right of the scale.
- Inducing physical change is slow and expensive.
- But once started, it’s easy to continue.
The Playground

Disk Arrangement
- A disk is a logical array of sectors.
- Sectors are arranged in a circular track on a platter.
- Coincident tracks on all platters form a cylinder.
- The logical sector index turns into a (cylinder, track, sector) triple.
- The disk controller performs the translation.
Access Costs
- Latency is the wait for the first bit (103 nsec).
- Delay is the wait for the last bit (10 nsec).
- Overall latency comprises
- seek latency on the arm, and
- rotational latency on the platters.
- Overall delay is read-write speeds.
- But watch out for caches and buffers.
Performance Requirements
- The best disk performance comes from exploiting locality:
- The next sector should be as close to this sector as possible.
- Accessing consecutive sectors is better than non-consecutive access.
- Combine several small requests into one large one.
- “Read i; read i + 1; read i + 2” vs
“Read i, i + 1, i + 2.”
- “Read i; read i + 1; read i + 2” vs
Disk Connections
- Disks connect to the system via the usual protocols (SATA, SCSI, USB, &c).
- Network area storage (NAS) connects to the system via the network (ethernet).
- Storage area network (SAN) connects to the system via a private network.
- SAN and NAS are larger than DAS (Tbytes vs Gbytes), and provide easier, more basic sharing.
Exploiting The Multitude
- Making an excessively big, fast disk is hard and expensive.
- Collecting an equivalent bunch of small cheap disks is easy.
- But how are a bunch of small, cheap disks arranged into a big, fast disk-equivalent?
- This is the problem solved by RAID (redundant array of inexpensive disks).
Combining Disks
- The “big” part of “big, fast” seems easy.
- Tying the disks together is essentially a mechanical problem.
- The “fast” part seems less obvious.
- There are two performance hits: latency and delay.
- Reducing latency is usually hard, so consider delay.
- How can n disks deliver the last bit more quickly?
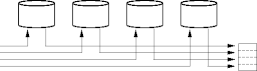
Exploiting Parallelism
- Reading a page from a disk does nothing for delay.

- Reading a page from n disks reduces delay by n.
An Alternative
- But what about reading several pages at the same time?
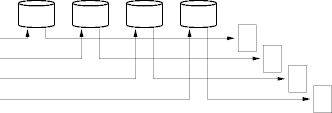
- This works if the page demand is high, and the page mapping is clever.
Data Striping
- Data striping exploits multiple disks using parallelism.
- Bit striping writes bytes to a factor or multiple of eight
disks.
- Disk i gets bit i of each byte.
- Block striping writes associated (file) blocks across the
disks.
- Block i goes to disk i mod n.
- There are many striping variants.
Striping Advantages
- Striping (block striping, mostly) exploits multiplicity to provide
- Load balancing: smearing pages across disks reduces per-disk
queuing.
- No queuing improves small request throughput.
- Parallelism: smearing associated pages across disks improves large request throughput.
- Load balancing: smearing pages across disks reduces per-disk
queuing.
Technology Advances
- Improving storage technology makes “big fast” less difficult.
- But electromechanical devices like disks still fail.
- The more disks are piled up, the more likely one of them’s going to fail.
- Fortunately, reliability comes from redundancy.
- And having many disks means much redundancy.
RAID Reliability
- RAID: redundant array of independent disks.
- RAID exploits the redundancy possible with many disks to provide
reliability.
- This trades-off performance for reliability.
- The RAID level determines how a RAID device
- resolves the performance-reliability trade-off, and
- exploits redundancy to get reliability.
RAID 0 and 1
- RAID 0 has no redundancy.
- All disks are used to store data.
- Raid 1 uses mirroring.
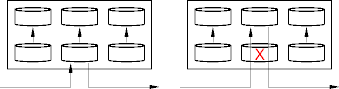
- RAID 1 has a 100% overhead.
Error Detection
- Single bit-flip errors have highest probability: 1 → 0 or 0 → 1.
- Parity counts 1 bits in a byte (bit string).
An even number of 1s: even (0) parity.
An odd number of 1s: odd (1) parity. - Single-bit parity detects
single-bit errors.
01010101+0 01010101+0 \(\downarrow\) \(\downarrow\) 01011101+0 01001101+0
Error Correction
- Parity detects but can’t correct a bit flip.
- Correcting a bit flip requires three extra (non-parity) bits.
00+000 01+011 10+101 11+110 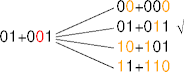
- STARTSIDEONTE(This) In particular, this is known as a distance three Hamming code because transforming one valid check-bit group to another valid check-bit group requires flipping two different bits. END-DELETING() is known as an error-correcting code (ECC).
RAID 2
- RAID 2 disks bit-stripe bytes across seven disks.

- Four data disks and three parity disks.
- The disk set forms an ECC over the data disks.
- The three-disk overhead varies with the data disks, but is usually less than RAID 1.
RAID 3
- External error detection makes possible one-bit error recovery.
010?0101+0 → 01010101+0
- Modern disks provide sector-level error detection.
- RAID 3 uses n - 1 data disks and a parity disk for reliability.
- Bit-striped bytes, but sector-level recovery.
But What of Latency?
- Reducing latency via technology is hard and expensive.
- Not so delay.
- Latency usually responds to cleverly using current technology.
- Load balancing, for example.
- File systems are mainly responsible for reducing latency.
Summary
- Disks provide an array abstraction with (cylinder, track, sector)
addressing.
- And involve persistence.
- Good performance requires handling latency and delay.
- Delay can be handled simply (more or less) with redunpdancy.
- From there come RAID devices.
- Handling latency is the file system’s responsibility.
Credits
- Papertape3.jpg from the Wikimedia Commons under a Creative Commons BY SA license.
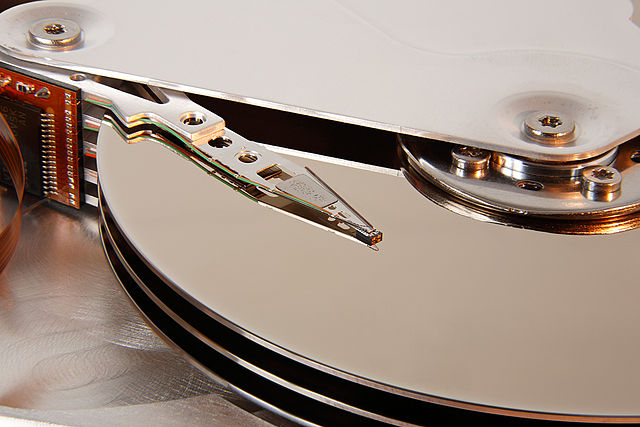
- 640px-Seagate-ST33232A-hard-disk-head-and-platters-detail.jpg by Eric Gaba from the Wikimedia Commons under a Creative Commons BY SA license.
| This page last modified on 2012 March 21. |

