Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes
31 January 2011 • Recursion
Outline
|

|
A Boxy Picture
- How do you draw this picture?
Investments
- Every year you can invest in a stock, or
every two years you can invest in a bond.- The same amount is invested every year.
- One active investment at any time.
- The expected return in year y is S(y) for the stock and B(y) for the bond.
- Based on expected returns, what investment strategy maximizes return over n years?
Choices
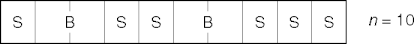
- Given { 1, 2, 3, 4 } (n = 4), how many ways are there to choose 2
numbers?
1, 2 2, 3 3, 4 1, 3 2, 4 1, 4 - Six, apparently.
- Given n distinct items, how many ways are there to pick i ≤ n items?
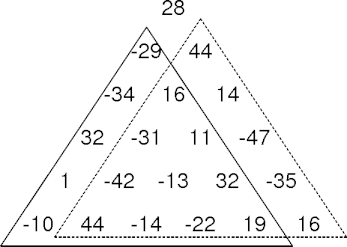
Finding Max Sum Paths
- Find the neighbor triangles’ max sum paths.
- Pick the neighbor with the larger max sum path.
Recursion
- General approach:
- Split a problem into smaller similar, subproblems.
- Repeat until the subproblems are trivial.
- “Trivial” means solved with no computation.
- Recombine subproblem solutions into a solution for the originating (sub)problem.
- This approach is called recursion.
Recursion Format
- The trivial subcomputation in step 2 is called the base case.
- The recursive steps 1 and 3
- Simplifies a problem into smaller similar subproblems.
- Recursively applies the algorithm to the subproblems.
- Combines the subproblem solutions into a more complete solution.
Recursion Advantages
- The advantages of exploiting recursion include:
- Simplicity: the trivial problem, dividing problems and recombining solutions.
- Wide applicability: recursion can be discovered in surprising places.
- Transparency: correct recursive algorithms are correct (almost) by inspection.
- Cliched: the same damn thing over and over.
Recursion Disadvantages
- Problems with recursion include
- Computational expense.
- Easily and (usually) automatically transformed into more efficient forms.
- Opacity, particularly among the uninitiated.
- Oh well.
- Subtle design errors.
- Few hiding places.
- Computational expense.
Finding Recursion
- Recursion relates directly to the problem’s structure.
- There are three general recursion sources:
- The problem or data structure; structural recursion.
- Linear structures; inductive recursion, a special case of structural recursion.
- optimized (usually) semi-recursive algorithms; degenerate recursion.
Structural Recursion
- Structural recursion is (almost) a gimme; it follows from the problem
or data structure.
- Although the problem or data structure may not be the best one to use.
- Examples:
- The max sum path problem: a triangle is an apex with left and right subtriangles.
- Trees: a tree is a node with a set of trees as children.
Recursive Data Structures
- A recursive data structure D is defined by
- A base case giving the simplest possible instance of D.
- A constructive case that combines one or more D instances and other data into a new, single D instance.
- A recursive algorithm undoes the structure created by the constructive
case.
- And stops recursing at the base case.
Example
- An n-ary tree of type T is
- Nothing (the base case).
- A value of type T and up to n n-ary trees of type T.
- A recursive algorithm:
bool find(v, root) if root == nil return false if root.value == v return true return find(v, root[0]) || ... find(v, root[n-1])
Inductive Recursion
- Inductive Recursion is structural recursion over linear
structures.
- Arrays, sequences, and the like.
- The subdivision is usually (but not always) into a single element and the rest of the structure.
- With care, inductive recursion can be automatically transformed into efficient looping code (tail-call optimization).
Example
- Find an element x in an array.
- Base case: finding an element in an empty array is trivial.
- Recursive case:
- Splint an n-element array into a 1-element array and an array with n - 1 elements.
- If x is in the 1-element array, return true.
- Otherwise, return the result of recursing on the array with n - 1 elements.
Example Code
bool find(x, a[])
if a.size == 0
return false
else
if a[0] == x
return true;
else
return find(x, a[1..a.size()])
Degenerate Recursion
- Sometimes extra information can be used to modify the recursive
structure to produce a better design.
- But possibly not producing something following the typical recursive pattern.
- Example: searching for x in an unordered array vs. an ordered array.
Unordered Array Searching
- No extra knowledge about an unordered array; use straight inductive
recursion.
bool find(x, a[]) if a.size == 0 return false n = a.size/2 if a[n] == x return true return find(x, a[0..n - 1]) || find(x, a[n + 1..a.size])
Ordered Array Searching
- The extra ordering information helps eliminate the subproblems.
bool find(x, a[]) if a.size == 0 return false n = a.size/2 if a[n] == x return true if a[n] < x return find(x, a[n + 1..a.size]) else return find(x, a[0..n - 1])
Recursion Requirements
- To use recursion successfully, should have
- A base case (a trivial subproblem).
- A way to divide the problem into subproblems.
- A way to combine subproblem solutions.
Recursive Design
- Make sure the base case is
- Really a base case (that is, a trivial instance of the problem).
- Is correctly solved.
- Make sure the recursive step
- Creates subproblems related into the original problem.
- Combines subproblem solutions into a solution for the larger problem.
Recursion Pitfalls
- Although it’s simple, it’s possible to get recursion
wrong.
- The base case is wrong, incomplete, or incorrectly solved.
- The subproblems are incorrectly derived from the original problem.
- Subproblem solutions are incorrectly combined into an invalid solution for the original problem.
Wrong Base Cases
- The base case for factorial is 0, not 1.
int
factorial(n) if n == 1 return 1 return n*factorial(n - 1) int factorial(n) if n == 0 return 1 return n*factorial(n - 1)
Incomplete Base Cases
- How many 3- and 5-cent stamps equal any amount over 7 cents?
- For example, 11 cents equals one 5-cent and two 3-cent stamps.
- The recursion seems easy:
- The base case is 8 = 3 + 5.
- For any value n > 7, n = n' + 3.
- One more 3-cent stamp than needed for n'.
Stamp Counting Code
- That seems easy enough; here’s the code.
int-pair stamps(n) if n == 8 return (1, 1) return (1, 0) + stamps(n - 3) - Unfortunately, this code is wrong. Why?
Revised Code
- There are three base cases:
8 = one 3¢ stamp + one 5¢ stamp.
9 = three 3¢ stamps + no 5¢ stamps.
10 = no 3¢ stamps + two 5¢ stamps.int-pair stamps(n) if n == 8 return (1, 1) if n == 9 return (3, 0) if n == 10 return (0, 2) return (1, 0) + stamps(n - 3)
Bad Subdivisions
- The subproblems must be strictly smaller than the original problem.
- If not, the recursion won’t terminate.
- The subproblems must be really related to original problem.
- Otherwise the subproblem solutions won’t be related to the original problem’s solution.
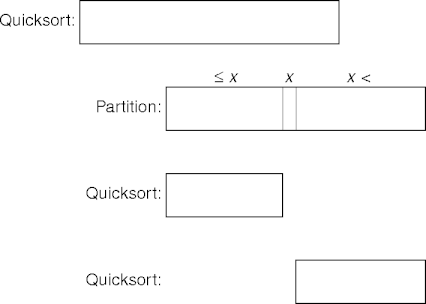
Quicksort
- Quicksort partitioning is slightly tricky code; getting it wrong breaks quicksort.
Improper Combinations
- Incorrectly combining correct subproblem solutions may lead to an incorrect original-problem solution.
- Given a set of planer points, find a pair with minimal distance
between them.
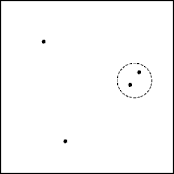
Closest Points
- Repeatedly divide the point set in half until each piece contains at
most two points.
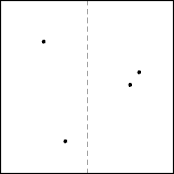
- For two points, return the points; otherwise return nothing.
- From each half select the closest pair and return the smaller of the two pairs.
- Unfortunately, this doesn’t work. Why?
Dividing Closest Points
- A closest pair of points may exist between divisions of the point set.
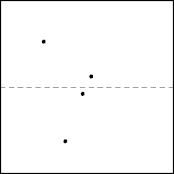
- Correctly recombining subproblem solutions requires more work than just comparing the subproblem solutions.
Extended Example
- Matrix addition.
- Recursion’s cost.
- Reducing recursion’s cost.
- Automatically.
- By hand.
Iterative Matrix Sum
- Given two n × n matrices, return their sum.
for row = 1 to n for col = 1 to n s[row, col] = a[row, col] + b[row, col] - Simple and fast.
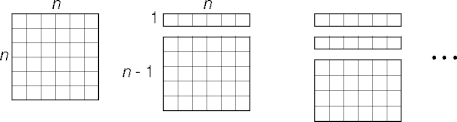
Matrix Decomposition
- A matrix is a row on top of a matrix, but what is a row?
- This decomposition is iterative.
Recursive Matrix Sum
- Is there a non-iterative decomposition?
row-by-row(row, n)
if row < n
col-by-col(row, 0, n)
row-by-row(row + 1, n)
col-by-col(row, col, n)
if col < n
s[row, col] =
a[row, col] + b[row + col]
col-by-col(row, col + 1, n)
row-by-row(0, n)
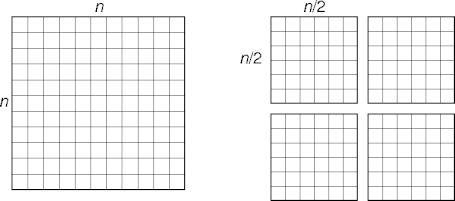
Another Matrix Decomposition
- Represent (sub-)matrices by their upper-left corner and size: x, y, n.
Another Matrix Recursion
- This code assumes n = 2i, i ≥ 0.
- The general case is similar but messier.
matrix-sum(a[], b[], x, y, n)
if n = 1
s[x, y] = a[x, y] + b[x, y]
else
n' = n/2
matrix-sum(x, y, n')
matrix-sum(x + n', y, n')
matrix-sum(x, y + n', n')
matrix-sum(x + n', y + n', n')
Which is Better?
- Which is better:
row-by-rowandcol-by-colormatrix-sum? - It depends:
-
row-by-rowandcol-by-colis complex but potentially as efficient as the nested-loop code. -
matrix-sumis less complex but unlikely to be as efficient.
-
Does It?
- 1024×1024 matrices, average of ten sums, standard deviations from 300 to 20,000 μsec.
- 1.6 GHz cpu, Debian testing, g++ 4.1.3.
- See the C++ code.
- In general,
matrix-sumloses. Why?
| C++, sec/sum | ||
|---|---|---|
| Method | -O0 | -O3 |
| loop | 0.71 | 0.27 |
| iterative | 0.66 | 0.24 |
| recursive | 1.50 | 1.10 |
Recursion’s Cost
- Why is recursion expensive at runtime?
Recursion
- Creates a bunch of subproblems.
- Solves each of the subproblems.
- Recursion’s cost comes from creating and then solving a bunch of
subproblems.
- Each activity has a run-time cost not incurred by the equivalent non-recursive code .
Implementing Recursion
- An recursion implementation has to deal with all those subproblems.
- Storing them and executing them.
- A limitation: only one executing (sub)problem per program
(single-threaded execution).
- Multiple executing (sub)problems are restricted to a small (≤ 64) total amount.
- Use the only tool we have: subroutines.
- That’s execution. What about storage?
Activation Records
- Given a function with local variables, where are the local variables stored?
- In a storage block called the activation record.
- But where are the activation records stored?
int f() int i, j double x // whatever
|
|
|
|
|
Activation Stack
- Procedures return in reverse calling order.
a() a() calls b() b() calls c() c() returns b() returns a() returns
- Use a stack, the activation (or run-time) stack.
Recursion’s Cost
-
The cost
of recursion is the cost of the subroutines.
- Executing the call and handling the storage.
- Calling is heavily optimized at the system and architecture level.
- But however cheap a call may be, not making a call is cheaper.
- Tail-call recursion can optimize the calls away.
Tail Calls
- A tail call a subroutine call made just before procedure exit.
row-by-row(row, n) if row < n col-by-col(row, 0, n) // not a tail call row-by-row(row + 1, n) // a tail call - A recursive tail call can be replaced by a branch to the subroutine start.
- This is known as tail-call optimization.
- The result is a loop.
Tail-Call Problems
- Not all recursion can be cast into tail-call form.
- The regularly recursive
matrix-sum().
- The regularly recursive
- Sometimes casting recursion in tail-call form makes it more complex.
- Compare
row-by-row()andcol-by-col()withmatrix-sum().
- Compare
- Unsuccessful tail-call optimizations leave recursive calls.
Explicit Storage Management
- When tail-call optimization fails, the recursion has to be manually removed.
- This involves (usually) an explicit loop over stored subproblems.
- Example: print the reverse of a singly-linked list.
rprint(link) if link ≠ nil rprint(link→next) print(link→data)
Example
- Recursion relies on procedure calls, procedure calls rely on the
run-time stack.
- Use a stack as the intermediate storage.
rprint'(link) for l = link; l ≠ nil; l = l→next stack.push(l) while not stack.empty() print stack.pop()→data
- Any data structure will do, as long as it preserves the proper order.
References
- Debunking the “Expensive Procedure Call” Myth (or Lambda: The Ultimate Goto) by Guy Steel, AI Memo 443, MIT, 1977.
- Considering Recursion by Arch Robison in Dr. Dobb’s Journal, March 2000.
- Gödel, Escher, Bach by Douglas Hofstadter, Basic Books, 1979.
Credits
| This page last modified on 28 August 2008. |