Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Notes
19 January 2011 • Introduction
Outline
- A problem and two solutions.
Three Questions
- The three questions underlying this course:
- How can this problem be solved?
Algorithm design.
- How to represent the problem and solution?
Data structures.
- How good is the solution?
Algorithm analysis.
- How can this problem be solved?
Number Triangles

Moves and Paths
- Number-triangle moves.
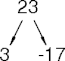
- Number-triangle path.
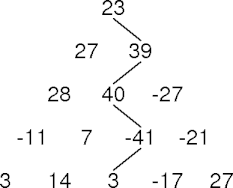
Path Sum
- The sum of the values along a path is the path sum.
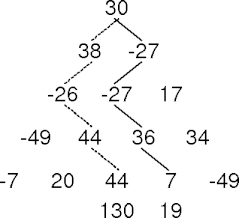
- Given a number triangle, find a path with maximum sum.
What's The Solution?
- Start with the problem.
- Given a numeric triangle.
- Find a triangle path with maximal sum.
- Now what?
- What does the problem say?
- Look for paths through the triangle.
- Keep a path with maximal sum.
- What does the problem say?
Is The Algorithm Good?
- Does this work?
- Look for paths through the triangle.
- Keep a path with maximal sum.
- Yes, assuming
- Path sums are computed and compared correctly.
- All possible paths are covered.
The Algorithm
max-sum-path(triangle)
all-paths = all-paths(triangle)
max-path = pick(all-paths)
max-sum = path-sum(triangle, max-path)
for each path in all-paths
sum = path-sum(triangle, path)
if sum > max-sum
max-sum = sum
max-path = path
return [ max-sum, max-path ]
What About Data Structures?
- What's a triangle? What's a path?
- What does the algorithm say?
- Triangles generate paths (
all-paths()). - Paths and triangles find sums (
path-sum()).
- Triangles generate paths (
- What does the algorithm say?
- Don't forget the problem.
- Triangles have numbers and are equilateral.
- Any data structures supporting this will do.
Are We Done?
- A triangle is a 2-D matrix.
- A path is a pair of arrays for rows and columns.
- Or an array of pairs. Or...
- A path set is an array of paths.
-
path-sum()is straightforward. - What about
all-paths()?
Finding Paths
- Correctness requires all paths be considered.
- The problem allows down and to left, down and to the right.

- Is there some structure we can exploit to organize path finding?
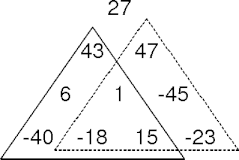
Path Structure
- All the paths are
- From the apex to all the paths in the left sub-triangle.
- From the apex to all the paths in the right sub-triangle.
Path Finding
all-paths(row, col)
if row == N
return [ (row, col) ]
left-paths =
all-paths(row + 1, col)
right-paths =
all-paths(row + 1, col + 1)
paths = []
for path in left-paths + right-paths
paths += (row, col) ++ path
return paths
Is The Algorithm Good?
- How long does the algorithm take to find a solution?
Triangle Solution size time μsec 5 251 10 6,270 15 267,000 20 8,620,000 25 283,000,000 - It's slow. Why?
How Many Paths Are There?
- Each row requires a choice between two directions.
- N rows leads to 2N - 1 possibilities.
- This is bad.
What's The Problem?
- How many times is the middle sub-triangle searched?
- There's lots of redundant work going on.
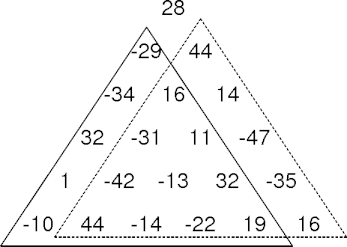
Avoiding Repeated Work
- How can the algorithm avoid repeated work?
- Does the work need to be repeated?
- A couple of important properties:
- The triangle is static; it doesn't change.
- A sub-triangle's max-sum path is independent of paths to the sub-triangle.
- Once the work is done, it stays done. Remember it.
Anything Else?
- There's still exponentially many paths generated.
- One final trick: there's no need to generated the paths from the top
down.

- Start at the base and work towards the apex.
- Still wasted work, but not nearly as much as before.
Algorithm Changes
- Keep a second array to remember max-sum paths.
-
path[r,i].pathis the max-sum path for the sub-triangle with apextriangle[r,i]. -
path[r,i].sumis the max-sum value for the path.
-
- Work from the base to the apex.
- No more path generation; no more repeated work.
A Faster Algorithm
max-sum-path(triangle)
for i = 1 to N
paths[N, i] = (triangle[N, i], [ (N, i) ])
for r = N - 1 to 1
for i = 1 to r
path = paths[r + 1, i]
if path.sum > paths[r + 1, i + 1].sum
path = paths[r + 1, i + 1]
paths[r, i] =
(path.sum + triangle[r, i],
(r, i) ++ path.path)
return paths[0, 0]
Is It Faster?
| Triangle | Solution Time μsec | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| size | All paths | Base up | ||||
| 5 | 251 | 434 | ||||
| 10 | 6,280 | 1,320 | ||||
| 15 | 267,000 | 2,330 | ||||
| 20 | 8,620,000 | 4,050 | ||||
| 25 | 283,000,000 | 9,080 | ||||
| 100 | 167,000 | |||||
| 500 | 6,750,000 | |||||
| 1000 | 36,400,000 | |||||
Summary
- Data Structures + Algorithms = Programs.
- But who is to be ruler: data structures or algorithms?
References
- The max-sum-path problem from Project Euler.
- A Scheme solution to the max-sum-path problem.
| This page last modified on 19 January 2011. |
