Outline
- Class descriptions.
- Interfaces
- Types
- Multiple Inheritance, interfaces, and traits.
An Array Class
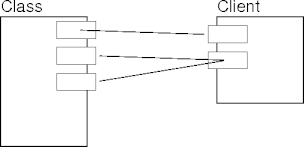
External Class Views
- A client looking at a class sees only the public methods made
available by the class.
- The set of public methods determines the way clients can interact with
a class.
Abstract Class Views
- The client can ignore everything but an class’s public methods.
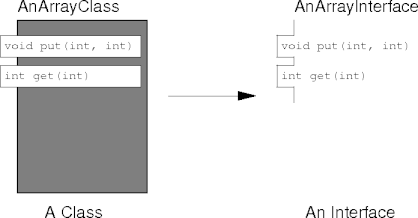
What’s Wrong With Classes?
- A class contains much information uninteresting to clients.
- Implementation details.
- Non-public methods and data.
- Uninteresting to clients, but necessary to implementers.
- Implementers and clients have different views of a class.
- And implementers win; how can clients win?
What’s Wrong With Classes??
- Other array-like classes have to be dealt with separately, rather than as
a related group.
- A permutation array looks just like an array, except.
- Is there a client-friendly way to specify the important parts of a
class?
- Is there a way to specify array-like behavior without specifying an array?
Interfaces
- An interface specifies a class’s client-visible features.
- Anything not visible at the interface doesn’t exist, as far as
the client’s concerned.
- This is a fiction, but a convenient one.
Interface Example
interface ArrayClass{
public void put(int i, int v)
public int get(int i)
public boolean find(int v)
// and so on
}
- With minimal implementer effort, the client sees only what matters.
Java Interfaces
- A Java interface contains method headers (called
signatures).
- No defined methods.
- All methods are non-static and
public.
- An interface can also contain variables, classes and other interfaces.
- Interface variables are
public static final.
- Interface classes (e.g.,
enums or Exceptions) are
public static.
Interface Examples
Interface Specifications
- Interfaces can be package-local (default) or public.
- Interfaces can extend other interfaces.
interface ChocolateBar
extends Candy {
ChocolateKind chocolateKind();
// and so on.
}
public interface ChocolateBar
extends Candy, 3DRectangle { ... }
Interfaces and Classes
- A class implements one or more interfaces.
class CustomArray
implements ArrayClass {
public void put(int i, int v) { ... }
public int get(int i) { ... }
public boolean find(int v) { ... }
}
Implementing Interfaces
- Implementing an interface is
an obligation
to define all methods in the interface.
- This is compile-time checked.
- Not defining interface methods is a compile-time fatal error.
Undefined Method Example
$ cat Colors.java
interface Colors {
public void red();
public void white();
void blue();
}
$ cat FlagColors.java
class FlagColors
implements Colors {
public void red() { }
public void white() { }
}
$ javac FlagColors.java
FlagColors.java:1: FlagColors is not abstract and does not
override abstract method blue() in Colors
class FlagColors
^
1 error
$
Classes and Interfaces
- A class may implement
- more than one interface.
- interfaces and extend a class.
- its own methods.
- An interface may extend another interface.
interface PrintableArrayClass
extends ArrayClass {
void print(Writer out);
}
Types and Operations
- An instance v’s type determines the allowable operations
on v.
- An instance v’s type doesn’t matter if nothing
operates on v.
- v’s type may as well be Object.
- Two extremes:
- perform no operations on v, or
- perform every possible operation on v.
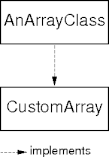
Interface and Class Types
- An interface defines a type.
- A class implementing an interface can considered to be of the
interface’s type.
|
|
- A value of type CustomArray can also be of type ArrayClass.
|
- Interfaces have other uses (such as pseudo multiple inheritance).
Interface Advantages
- An interface precisely specifies the constituent operations required by
a data structure.
- A
CustomArray behaves like an ArrayClass.
- A single interfaces covers many different but similarly behaved data structures.
Trait-Defining Interfaces
- Use interfaces to define traits: small, well-defined
collections of behavior.
interface Comparable
int compareTo(Object o);
public interface Destroyable
void destroy();
boolean isDestroyed();
public interface Readable
int read(CharBuffer cb);
Trait Behaviors
- Mix and match traits to give desired behaviors to classes.
class Card
implements Comparable
int compareTo(Object o) { ... }
// and so on.
class SecurityCertificate
implements Destroyable, Readable
void destroy() { ... }
boolean isDestroyed() { ... }
int read(CharBuffer cb) { ... }
// and so on.
Trait Specifications
- Use traits to specify exactly and minimally what behavior class
instances should have.
boolean beats(Comparable x) { ... }
void validate(Destroyable tag) { ... }
Message read(Readable input) { ... }
- The same class instance may have several roles based on traits.
SecurityCertificate ticket =
new SecurityCertificate()
validate(ticket)
Message m = read(ticket)
Summary
- Interfaces specify expected class behavior.
- Specify a data structure’s constituent operations in terms of
interfaces.
- Think in terms of traits when defining interfaces.
References
-
Interfaces, Chapter 9 in The
Java Language Specification, 3rd ed. by James Gosling, Bill Joy, and Gilad
Bracha, Addison-Wesley, 2005.
- Interfaces and Inner Classes, Chapter 6 in Core Java, vol. 1, 8th
ed. by Cay Horstmann and Gary Cornell, Prentice Hall, 2008.
- Use interfaces only to define types, Item 43, from
Effective Java,
second edition, by Joshua Bloch, Addison-Wesley, 2008.
|
This page last modified on 24 January 2011.
|

|





