Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture Notes
18 February 2010 • Java Collections
Outline
- The Java Collection Framework.
- Interfaces
- Implementations
Collections
- The Java Collection Framework (JCF) contains
- Interfaces describing collection behavior.
- Implementation classes providing data structures.
- Abstract classes for other implementations.
- Also other odds and ends: backwards compatibility, adapters, and such like.
Objectives
- Gather and organize several related and common data structures.
- Gather and organize along object-oriented (polymorphic) lines.
- Provide a structure for developing other, more specialized data structures.
- Provide a mechanism for decoupling system components via consistent abstractions.
- Design and implementation leverage.
Collection Interface Hierarchy
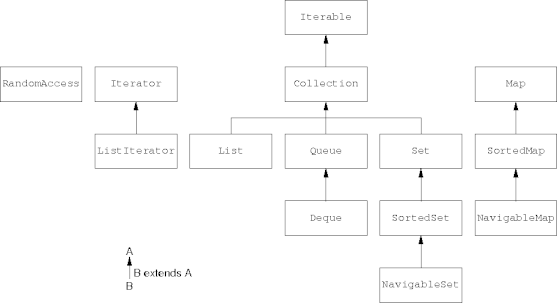
Collection Interface
- A group of elements (objects).
- Elements are ordered or not, duplicated or not.
- The interface is generic in the element type.
- The
Collectioninterface extends theIterableinterface.- Collections respond to the for-each statement.
The Collection Interface
interface Collection<E>
implements Iterable<E> {
boolean add(E e)*
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)*
void clear()*
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean equals(Object o)
int hashCode()
boolean isEmpty()
Iterator<E> iterator()
boolean remove(Object o)*
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)*
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)*
int size()
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
}* Optional
Optional Methods
- The element adding and removing methods are optional.
- Some collections are immutable.
- Collection implementations should throw a
UnsupportedOperationExceptionwhen inapplicable optional methods are called.
Group Methods
- Some Collection methods accept a collection of elements and operate
over the whole data set.
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)s.containsAll(c)returns true if everything incis ins.boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)s.removeAll(c)removes fromseverything inc.boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)s.retainAll(c)removes fromswith everything not inc.
Group Method Examples
- Let
sbe[ 1 2 3 ].s.containAll([ 1 3 ])returns true, leavessunchanged.s.containAll([ 3 4 ])returns false, leavessunchanged.s.removeAll([ 1 3 ])returns true,swill be[ 2 ].s.removeAll([ 3 4 ])returns true,swill be[ 1 2 ].s.removeAll([ 4 ])returns false, leavessunchanged.s.retainAll([ 1 3 ])returns true,swill be[ 1 3 ].s.retainAll([ 3 4 ])returns true,swill be[ 3 ].s.retainAll([ 4 ])returns true,swill be[ ].
Group-Method Implementations
-
containsAll()can be implemented using Collection interface methods:boolen containsAll(Collection<?> c) for (Object o: c) if (!contains(o)) return false return true - What about
removeAll()andretainAll()? Can they too be implemented using Collection interface methods?
Collection Interface Hierarchy
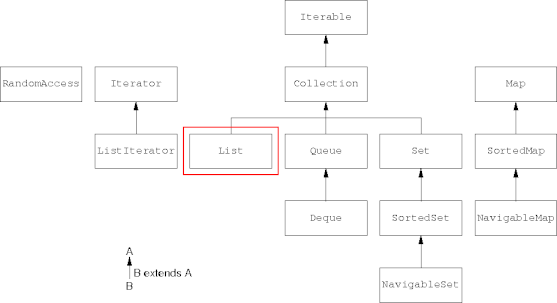
List Interface
- The
Listinterface tries to be general over sequences.- In particular, it wants to cover indexible as well as non-indexible sequences.
- The List interface also tries to be implementation independent.
- As a result, the List interface is somewhat complex to navigate and understand.
The List Interface
interface List<E>
extends Collection<E> {
boolean add(E e)
void add(int index, E element)
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
void clear()
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean equals(Object o)
E get(int index)
int hashCode()
int indexOf(Object o)
boolean isEmpty()
Iterator<E> iterator()
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
ListIterator<E> listIterator()
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
E remove(int index)
boolean remove(Object o)
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
E set(int index, E element)
int size()
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
}
Indexible List Methods
- What happens if the underlying implementation doesn't support indexing,
or provides expensive support?
- Optional methods (
set(), for example) can be skipped. - Required methods (
get(), for example) have expensive (linear) implementations.
- Optional methods (
Collection Interface Hierarchy
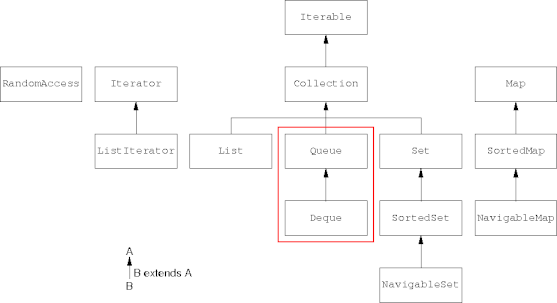
The Queue Interface
interface Queue<E>
extends Collection<E> {
boolean add(E e)
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
void clear()
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
E element()
boolean equals(Object o)
int hashCode()
boolean isEmpty()
Iterator<E> iterator()
boolean offer(E e)
E peek()
E poll()
E remove()
boolean remove(Object o)
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
int size()
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
}
The Queue Interface
- The
Queueinterface extends theCollectioninterface.Throws Returns exception special value Insert add(e)offer(e)Remove remove()poll()Examine element()peek() - The behavior of the two method groups differs on error conditions.
The Deque Interface
- The
Dequeinterface extends theQueueinterface.- It adds front and back versions of the
Queueoperations.addFirst(e), removeFirst(), getFirst() offerFirst(e), pollFirst(), peekFirst() addLast(e), removeLast(), getLast() offerLast(e), pollLast(), peekLast()
- It adds front and back versions of the
Collection Interface Hierarchy
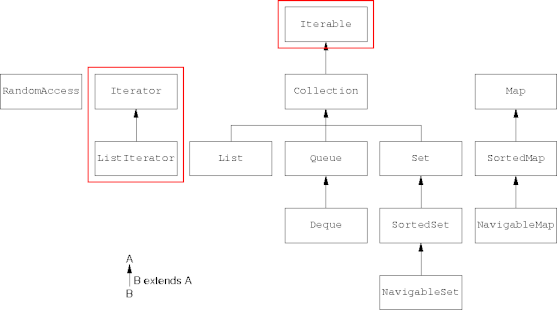
The Iterator Interface
- Example use:
final Iterator i = c.iterator() while (i.hasNext()) f(i.next())
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext()
E next()
void remove()*
}
* Optional
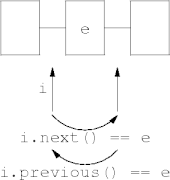
List Navigation
- The
next()andprevious()methods- move the iterator appropriately and
- return the element moved over.
List Iterators
- The Iterator interface sacrifices features for generality.
- It doesn't do much, but it applies widely.
- The ListIterator interface extends the Iterator interface to provide
more features.
- Bi-directional navigation (next and previous).
- In-traversal list modifications.
- More control over list positioning (indexing).
The List Iterator Interface
public interface ListIterator<E>
extends Iterator<E> {
void add(E e)*
boolean hasNext()**
boolean hasPrevious()
E next()**
int nextIndex()
E previous()
int previousIndex()
void remove()*, **
void set(E e)*
}
* Optional, ** From Iterator
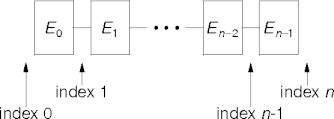
List Iterator Indexing
- ListIterator (or cursor) positions lie between adjacent list elements.
- Or before the first element or after the last element.
List Manipulations
- A new element is added before the next or after the previous element.
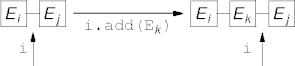
- Adding to an empty list is easy.
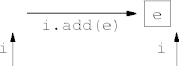
Removing Elements
-
remove()removes the element returned bynext()orprevious().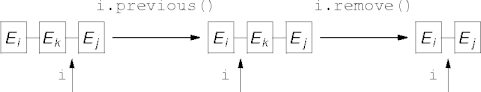
-
next()orprevious()must be called before each call toremove().
Better Iteration Code
- Iterating over values is such a common activity that having to write
final Iterator i = c.iterator() while (i.hasNext()) f(i.next())
(or similar) every time is poor design.
- Package iterations in a more abstract for-each loop form:
for (T e: c) f(e)
The Iterable Interface
- The Iterable interface indicates a class that can iterated over using
for-each loops.
public interface Iterable<E> { Iterator<E> iterator() }- Essentially: here's the iterator you need, without all the details.
- Classes not implementing the Iterable interface cannot partake in for-each loops.
Interface Declarations
- Remember: for greatest flexibility, use the highest (most abstract) interfaces possible as variable types.
- From high to low:
Collection<Integer> pending = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); Queue<Integer> pending = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); Deque<Integer> pending = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
Implementation Hierarchy
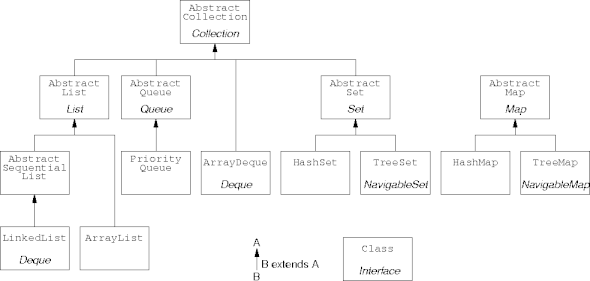
Abstract Implementations
- The more practical collection interfaces contain many method
definitions.
- Implementing classes have to implement them all, if only to fail when called.
- The abstract implementation classes provide a skeleton
implementation for further development.
- The concrete class is a child of the abstract implementation class.
Example
- The
AbstractQueueclass implements theQueueinterface.public abstract class AbstractQueue<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Queue<E>
- It contains around 40 methods.
- The
PriorityQueueextendsAbstractQueue.public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements
Serializable
Linked Lists
- The
LinkedListclass extends theAbstractSequentialListclass. - The interfaces specify a doubly-linked list.
- The
AbstractSequentialListclass assumes a dynamic link implementation.- That is, indexing is expensive.
Array Lists
- The
ArrayListclass implements a linked list assuming indexing is cheap.- That is, an implementation based on dynamic arrays.
-
ArrayLists are more efficient than areVectors.- But
ArrayLists aren’t thread safe andVectors are.
- But
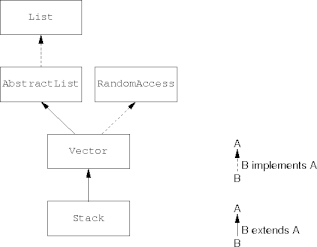
Random-Access Iterators
- The
RandomAccessinterface indicates efficient indexing.- Faster:
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) f(lst.get(i))
- Slower:
for (Iterator i = lst.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) f(i.next())
- Faster:
-
RandomAccesscontains no methods; it just flags classes with efficient indexing.
Priority Queues
- The
PriorityQueueclass stores elements in increasing priority order (a min-priority queue). - The queue elements can implement the
Comparableinterface. - A queue can be created with a
Comparatorimplementing, overriding the element comparable, if any.
Where’s Stacks?
-
Stacks were added to Java before the Collection Framework (v. 1.0 vs v. 1.2).
Summary
- The Java Collection Framework designs and implements a group of common data structures.
- Declare variables with the most abstract interface type possible.
- Keep in mind that retreiving a value through a list iterator also moves the iterator.
References
- Collections (Chapter 13), Core Java vol. 1 eighth ed. by Cay Horstmann and Gary Cornell, Prentice Hall, 2008.
- The Java Collections Trail by Josh Bloch, Sun Microsystems.
| This page last modified on 17 February 2010. |
