Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture Notes
21 September 2010 • Classes and Abstract Data Types
Outline
- Arrays
- Classes
- Abstract Data Types.
- Classes and Abstract Data Types.
Array Definition
- An array is a sequence of element values.
- Each element has type T (arrays are homogeneous).
- An array of T (or a T array).
- The sequence size is fixed at n ≥ 0.
- An n-element T array.
- Elements in an n-element array are indexed by the integer set {
0, ..., n - 1 }.
- What about 0-element arrays?
Array Properties
Arrays- are fast and efficient to implement and use.
- Decades of hardware optimization.
- Heap-allocated arrays tend to blunt this property.
- have a simple and uniform cost model.
- Arrays provide constant-cost random access.
- throw exceptions when invalid indexes are used.
- And at other times too.
Array Operations
- Element access via the
[ ]operator.-
primes[i] = numbers[j]
-
- Determine array size via the
lengthfield (sorta).-
final int n = primes.length
-
- Traverse the elements in order (0 to n - 1).
-
for (int p: primes) f(p)
-
- See the
Arraysclass for lots more.- Copying, sorting, searching, converting, …
Array Example
int [] collapse(int a[], int x) {
// Suppress runs of x in a.
// collapse([0,0,1,1,0,0,0], 0) = [0,1,1,0]
final int n = a.length;
int cpy [] = new int [n];
int next = 0, i = 0;
while (i < n) {
cpy[next++] = a[i];
if (a[i++] == x)
while ((i < n) && (a[i] == x))
i++;
}
return Arrays.copyOf(cpy, next);
}See the code
Classes
- A class is a collection of data (state) and operations on the data.
- Class declarations have the form
class: [ modifiers ]? class ClassName [ modifiers ]?
{[ declaration ]*}declaration: instanceVariable | method | constructor - As in C++, there is no need to declare class components before use.
- Declarations may be ordered as desired.
Class Example
class AnArray {
// blah blah blah
}
Methods
- A class may have zero or more methods representing model interactions.
- Method declarations have the format
method: [ modifiers ]? returnType methodName([ arguments ]?) { ... }arguments: argument [,argument ]* argument: [ modifiers ]? type argumentName - Conventionally, a method name is camelCase with a lower-case first letter.
Method Example
class AnArray {
void put(int i, int e) { ... }
int get(int i) { ... }
}
Constructors
- A constructor is a special method that creates class instances.
- Constructor declarations have the format
constructor: [ modifiers ]? ClassName
([ arguments ]?) {...}- There’s no return type and the method name is the class name.
Default Constructors
- Every class must have at least one constructor.
- A class without an explicitly declared constructor gets a
default constructor.
- It accepts no arguments and does nothing.
- Explicitly declared constructors inhibit the implicit default
constructor.
- Unlike C++, this is usually not a problem.
- Explicitly declare a default constructor if it is.
Instance Variables
- A class may have zero or more instance variables representing model state.
- Instance variable declarations have the format
instanceVariable: [ modifiers ]? type variables
;variables: variable [,variable ]* variable: variableName [=initializer ]? - Conventionally, a variable name is camelCase with a lower-case first letter.
Instance-Variable Example
class AnArray {
void put(int i, int e) { ... }
int get(int i) { ... }
private int size;
private int elements [];
}
Class-Component Access
- A class’s non-constructor methods and instance variables
(collectively known as the class’s fields) are accessed using
dot notation:
classInstance.fieldName
-
Unlike C++,
the only reason to access a Java class method is to call it.
classInstance.methodName
(arg, ...)
Instance Variable Initialization
- Java requires that every variable always contain a defined value.
- “Defined” does not mean “sensible”.
- It means (among other things) non-garbage.
- When instance variables are created, they have to be initialized
to obey this property.
- The compiler helps you maintain this property.
Default Initialization
- Instance variables without explicit initialization receive a default
value at class-instance creation.
class AnArray { // blah blah blah private int size; private int elements[]; } - The default value depends on variable type.
Explicit Initialization
- Explicitly-initialized instance variables receive the computed value.
class AnArray { private int size = 0; // and so on. } - The initialization value is computed at each instance creation.
Constructor Initialization
- Instance variables can also be initialized in constructors.
class AnArray { AnArray(int n) { size = n; elements = new int [n]; } private int size; private elements[]; }
Abstract Data Types
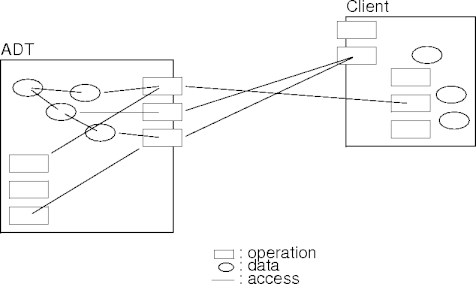
- An abstract data type (ADT) is also a collection of data and operations on the data.
- An ADT defines a strong partition between accessible and inaccessible components.
- All components are accessible within an ADT.
- Only selected components are accessible outside the ADT.
- Accessible by the ADT’s client.
- “Strong” means compiler supported.
ADT Interfaces
- An ADT interface defines the partition between accessible and inaccessible components.
- The interface lists all the operations accessible outside the ADT.
- Operations not listed in the interface are inaccessible outside the ADT.
- Everything else not listed by the interface is inaccessible too.
- In particular, data is inaccessible outside the ADT.
ADT Operators
- ADT interface operators divide into:
- Query operators: read-only operators that answer questions.
- Examples:
size(),find(),isEmpty().
- Examples:
- Manipulation operators: read-write operators that manipulate state.
- Examples:
add(),remove(),sort().
- Examples:
- Maintenance operators: read-write operators that change the ADT itself.
- Examples:
new(),free(),resize().
- Examples:
- Query operators: read-only operators that answer questions.
ADT Example
Classes and Abstract Data Types
What’s the difference? Why have both?- ADTs are a concept; classes are an implementation.
- ADTs provide stronger access guarantees than do classes.
- ADTs got there first, but didn't win the race.
- ADTs are simpler than are classes (no inheritance).
What An Array Can Do
- What operations does an array support?
- Maintence:
create(),free(),resize(), ... - Query:
get(),size(), ... - Manipulation:
put(),swap(), ...
- Maintence:
- There's no information about how the array is implemented, just
how it behaves.
- That is, the operations it supports.
An Array ADT
class ArrayADT {
ArrayADT(int n) { ... }
void resize(int n) { ... }
int get(int i) { ... }
int size() { ... }
void put(int i, int, v) { ... }
void swap(int i, int j) { ... }
// and so on.
}
Summary
- Classes group data and data operations into an organized unit.
- An abstract data type also groups data and data operations into an
organized unit.
- But with stronger, simpler organization then that of classes.
- Abstract data types are a concept; classes are an implementation.
References
- On Understanding Data Abstraction, Revisited by William Cook, OOPSLA 2009.
| This page last modified on 21 January 2010. |
