Object-Oriented Programming with Java Lecture Notes
10 February 2009 • Types
Outline
- Java types.
- Primitive and reference types.
- Array and String types.
Java Types
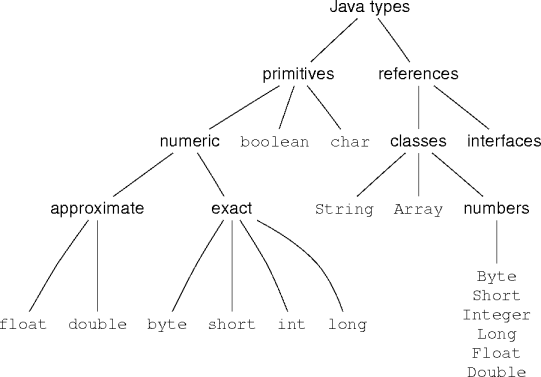
Booleans
- A boolean is one-bit value.
- The literals are
trueandfalse. - Java separates boolean values and other type values.
- In particular, integers are not booleans and vice versa.
- C++ (and C) is considerably looser.
Characters
- A char value is a 16-bit unsigned value representing a Unicode code point.
- Character literals can be characters (
'a'), Unicode escapes ('\uxxxx'), and a small set of letter escapes ('\t'). - Java characters are not convienent small integers as in C or C++.
- It’s best to use them as characters, and avoid using characters.
Exact-Number Types
- The exact-number types represent n-bit two’s compliment integers.
Name n literal byte8 1short16 -1int32 0long64 0Lor0l- No unsigned types.
Approximate-Number Types
- The approximate-number types represent 32-bit (
float) or 64-bit (double) IEEE-754 floating-point numbers. -
floatliterals end inforF;doubleliterals end in an optionaldorD.1f,3.14,-0.271e+1D - The approximate-number types also include the non-numeric values positive infinity, negative infinity and NaN (not a number).
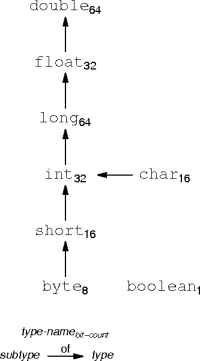
Primitive-Type Relations
- A subtype is compatible with its type.
- A subtype value can replace a type value.
- Neither relation is reversible, although both are transitive.
|
|
|
Primitive-Type Conversions
| target type | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
byte |
char |
short |
int |
long |
float |
double |
|
byte |
|||||||
char |
|||||||
short |
|||||||
int |
|||||||
long |
|||||||
float |
|||||||
double |
|||||||
| : Compatible. | t = s |
|
| : Cast required (with possible loss). | t = (t) s |
|
| : Compatible with possible loss. | t = s |
Java Types
Reference Types
- A Java reference type is analogous to a C++ pointer to class
instance.
- Except: no touching.
- All accesses to Java class instances are through reference values.
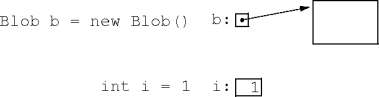
Primitives vs. References
- Primitive types are incompatible with reference types.
-
Will this method compile?
void m() {Objecto = 42; }
Primitives as References
- A primitive has to be converted to a class instance to be treated as a
reference.
void m() { Object o = newInteger(42); }
References as Primitives
- Similarly a reference has to be converted to a primitive.
- Using
primitive-typeValue()injava.lang.Number. - This is known as unwrapping the primitive.
void m(String key) { if (hashTable.containsKey(key)) int i = ((Integer) hashTable(key)).intValue(); } - Using
Automatic Conversions
- Wrapping and unwrapping primitives manually is a pain.
- And necessary prior to Java 5.
- Java 5 automatically converts between primitive-type values and
Numbers.
- The conversions are called autoboxing (wrapping) and
auto-unboxing (unwrapping).
- Usually omit the “auto”.
- The conversions are called autoboxing (wrapping) and
auto-unboxing (unwrapping).
Boxing Examples
void m() {
Object o = 42;
}
void m(String key) {
if (hashTable.containsKey(key))
int i = hashTable(key);
}
Arrays
- The Java Array is a class with some syntactic
sugar.
- The
[]access operator.
- The
- Arrays are fixed-size and 0-origin indexed.
- An n-element array has indices 0 through n - 1.
- Every array access is checked valid indices.
- Out-of-bound array accesses halt the program.
Array Declarations
- A variable
areferencing an array of elements of type T has the declarationT
[] aor Ta[]- An array declaration does not create an array instance.
- The array dimension is not part of the type.
- Multidimensional arrays have a similar declarations.
T
[][] aor Ta[][][]
Array Instance Construction
- Array construction is similar to other class construction.
- One difference is the array dimension.
int [] ia = new int [10];
char ttt[][] = new char [3][3];
- A one-dimensional array is constructed with elements set to null.
Array Initialization
- An array can be implicitly constructed and explicitly initialized with
bracket notation.
StringBuffer segs[] = { new StringBuffer(), new StringBuffer(), new StringBuffer() }; char ttt[][] = { { ' ', 'x', 'o' }, { ' ', 'x', 'o' }, { 'x', 'o', ' ' } };
Anonymous Arrays
- An array can also be explicitly constructed and initialized.
int p[] = int [] { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 };- No explicit dimension sizes are given.
- The expression T
[]initializer is a convenient way to construct an anonymous array.t.sum(int [] { 1, 2, 3 });
Array Structure
- An array of reference types is an indirection structure.
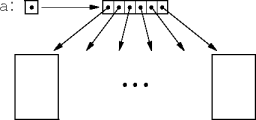
- Each array element must be explicitly initialized to a class instance.
- Multi-dimensional arrays follow recursively.
- An array of primitive types has a flatter structure.
An Array Idiom
- Methods can return arrays.
point [] getOutliers(double mean, double stdDev) { /* blah blah blah */ } - What should the method return if there’s no elements to return?
- A null reference.
- A zero-element array.
Favor Zero-Element Arrays
- Returning a null requires a null test before accessing the result.
result = data.getOutliers(m, sd) if (result != null) for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) // blah blah blah - Returning a zero-element array requires no testing.
result = data.getOutliers(m, sd) for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) // blah blah blah
Strings
- A String is a sequence of zero or more Unicode
“characters.”
- A sequence, not an array (that is, no
[]).
- A sequence, not an array (that is, no
- String literals are enclosed in double quotes.
- The
Stringclass has around 70 methods for handling strings.- Set your IDE to browse the API docs.
- Become familiar with
Stringmethods.
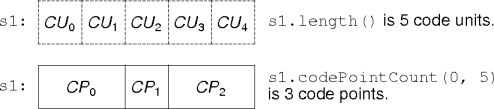
Code Units vs Code Points
- Unicode characters are called code points.
- A code point is one or more code units.
- A code unit is a 16-bit value corresponding to a Java
char. - So what?
String Equality
- If
s1ands2are strings, what doess1 == s2do?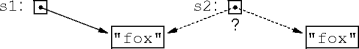
- What does
s1.equals(s2)do?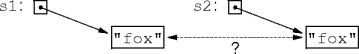
- This confusion isn’t limited to strings.
String Immutability
- A string instance is immutable; it can’t be changed.
- Immutability makes mutating string operations expensive.
- Lots of class-instance creation and data copying.
-
Favor
StringBuilders overStrings for manipulating strings.- Less copying, less instance creation.
Immutability Example
- Consider
s += "!"for strings.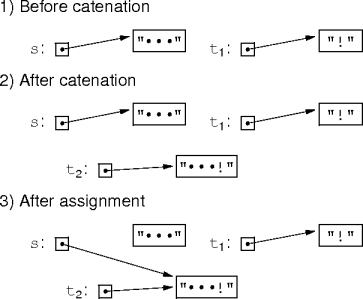
Mutability Example
- Consider
sb.append("!")for string buffersb.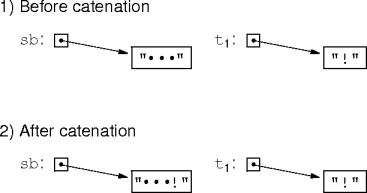
Catenation Performance
- Read the contents of a text file into a string.
do ??? while not in.eof
- For a 1,000 line, 80 char/line file,
s += in.read()1.1 sec sb.apend(in.read())0.17 sec - String buffer expansion costs are assumed amortized linear.
The toString() Method
- The instance method
StringtoString()returns a printable representation of a class instance.- It’s a method from
Object, not fromString.
- It’s a method from
- It’s a good idea
to implement
toString()for significant classes.employeeName.toString()→
"EmployeeName@1cd2e5f", not so good.
employeeName.toString()→
"George Leroy Tirebiter", better.
Summary
- Java distinguishes primitive and reference types.
- Not so much since Java 5, but still...
- Arrays accesses are run-time checked and throw exceptions on
violations.
- Do not catch and ignore array-bounds exceptions.
- Be careful with string handling.
- Particularly with string catenation.
References
- Joel Spolsky’s Guide to Unicode.
- Items 9 (Always override
toString) and 27 (Return zero-length arrays, not nulls) from Effective Java by Joshua Bloch, Addison-Wesley, 2001.