Object-Oriented Programming with Java Lecture Notes
3 March 2009 • Exceptions
Outline
|

|
Errors
- What happens if there’s an error in a constructor?
Blob b = new Blob();
- What happens if something goes wrong way down there?
- Way down deep in a library.
- What’s the code to do?
The Error Pass-Along Problem
- The code at the error source may not be able to handle the error.
- Unknown context makes error handling difficult.
- Printing an error message and dying is helpful, but not always useful.
- Give up (after local clean-up, if needed) and pass the error along.
- Better, but how?
Error Return
- Methods can return error-status values.
Error e = ci.m(); if (e.status == Error.ok) { ... }- Complicates value-returning methods.
- Constructors can’t return any values.
Error Parameters
- Pass error values through method parameters.
void m(args, Error error) { ... } ci.m(..., e) if (e.status != Error.ok) { ... } - Not object pure.
- Or setter-getter clumsy if it is.
- Works for constructors.
Error Globals
- Use a global to pass error values.
ci.m(); if (error.status != Error.ok) { ... } - Not well structured, not thread safe.
Exceptions
- Exceptions provide an alternative mechanism for delivering error indications.
- Exceptions are not propagated along parameters, return values, or
globals.
- This is known as out-of-band communication.
- Uninterested code can chose to ignore exceptions.
- But, alas, it’s not that simple.
Exception Basics
- Each method call has a stack frame.
- The stack frame holds parameters, local variables, and other things related to the method. call
- The call stack contains the stack frames of all current method calls
- When one one method calls another, the called method pushes its stack frame on the call stack.
- When the top method returns, it pops its call stack frame off the call stack.
Call-Stack Example.
- Consider
int main () { ci.f() } int f() { ci.g() } int g() { if (b) ci.g() } - Initially
main()is called, ande()callsf().
Call-Stack Example..
-
f()then callsg().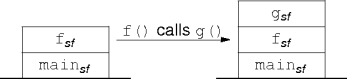
- Eventually
f()andg()return.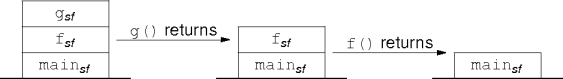
-
main()returns and the program ends.
Exceptions and the Call Stack
- The top of the call stack can throw an exception.
- This terminates the throwing method, popping it from the call stack.
- Each new call-stack top may catch the exception, or let it pass.
- Catching the exception continues execution at the catching method.
- Letting the exception pass terminates the method, popping it from the call stack.
Stack Unwinding
- Popping the call stack because of exceptions is known as unwinding the call stack.
- Completely unwinding the call stack terminates the program.
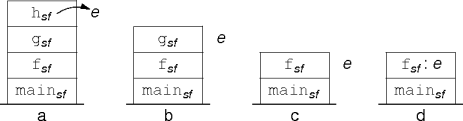
Exception Problems
- Exceptions are completely different from everything else.
- Another new and different thing to watch.
- Coordinated exceptions among independent modules requires work.
- Which methods throw what exceptions when?
- Unwinding the call stack is violent: it may occur unexpectedly, and the consequences are severe.
Basic Exception Mechanisms
- Java has three components for dealing with exceptions:
- The
throwstatement throws exceptions. - The
tryblock delimits exception handling. - The
catchblock catches exceptions.
- The
- There are other components too.
The throw Statement
- The
throwstatement signals (throws, raises) an exception:throwexception-ref;- Like
returnin syntax and semantics.
throw new NullPointerException(); final NullPointerException e = new NullPointerException(); throw e;
- Like
The catch Block
- A catch block catches thrown exceptions:
catch (ex-type ex-name) {body}- This syntax is similar to a one-parameter method definition.
catch (ExceptionType e) { // blah blah blah } - ex-name is accessible only within the catch body.
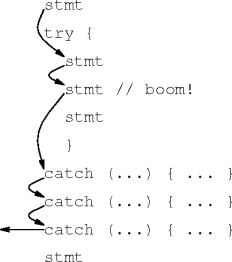
The try Block
- An exception can be caught only when it’s thrown from within a try
block:
try {body}- An exception thrown outside a try block immediately unwinds that method.
- A try block is its own scope.
- Variables declared in a try block are inaccessible outside it.
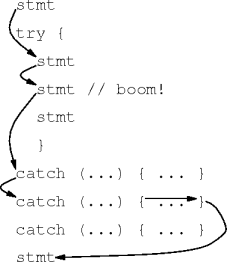
Try-Catch Statements
- A try block and
one or more catch blocks
from a try-catch statement:
try { body } catch ( ex-type ex-name ) { body } catch ( ex-type ex-name ) { body } // and so on - This is the basic exception-handling unit.
Normal Try-Catch Control
|
|
Handled Exceptions
- Immediate but normal try-block scope exit.
- An exception is considered handled as soon as a match is found.
catch body,
continue after the try-catch statement.
Example
- Assuming the catch block doesn’t throw another exception.
Unhandled Exceptions
|
|
Exception Clean-Up
try {
// state set-up
ci.g()
// state tear-down
}
catch (...) { ... }
catch (...) { ... }
ci.g()’s exception interrupts state tear-down.
- Duplicate code in the catch blocks.
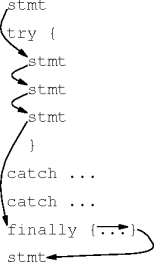
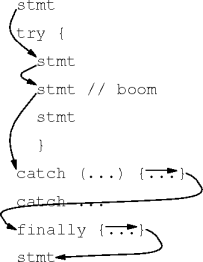
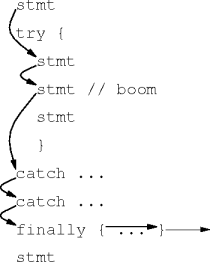
finally Blocks
- A try-catch statement’s finally block
finally { code }is always executed, exception or not, exception handled or not.
try { // state set-up ci.g() } catch (...) { ... } catch (...) { ... } finally { // state tear-down }
Finally Examples
|
|
|
|
| none | handled | propagated |
Matching Exceptions
- Exceptions match using assignment compatibility.
- A catch block with exception type ET catches exception of type TET when TET is an descendant of ET.
- The first matching exception wins, not the closest.
- Order the exceptions from most specific to most general in a try-catch statement.
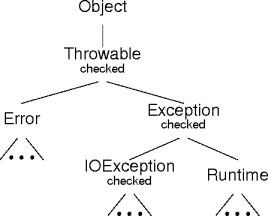
The Exception Hierarchy
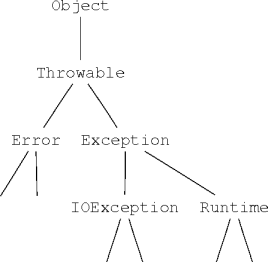
The Throwable Ancestor
- The
Throwableclass is the top of the exception hierarchy. - Has constructors
Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) Throwable(String message) Throwable(Throwable cause) Throwable()
- Also the expected getters and setters.
- See the JavaDoc API page for more details.
The Error Class
- The
ThrowablechildErrordefines abnormal conditions.- “Abnormal” means end-of-the world conditions, internal failures, and the like.
- Applications should ignore Error-based exceptions, and should not throw
them.
- The situation's so bad, nothing works anyway.
- Example
Errorchildren includeVirtualMachineErrorandAssertionError.
The Exception Class
- The
ThrowablechildExceptiondefines undesirable conditions the application should handle.- Or at least react to.
-
Exceptionis a useful catch-all in a catch block. - Applications should throw leaf
Exceptiondescendants.- Throw as much information as possible to help recovery.
Exception Children
- The
ExceptionchildIOExceptiondefines undesirable conditions related to input-output operations.- Examples include
FileNotFoundExceptionandEOFException.
- Examples include
- The
ExceptionchildRuntimeExceptiondefines undesirable conditions related to non-I/O execution.- Examples include
ClassCastExceptonandNullPointerException.
- Examples include
The Exception Hierarchy
-
Throwable: exception root.Error: neither thrown nor caught.Exception: checked exception root. (almost)Runtime: unchecked exceptions.
|
|
|
Avoidable vs. Fateful Occurrences
- An avoidable occurrence is one that could be prevented with a
reasonable amount of care.
- A null-pointer reference is an avoidable occurrence.
- So is an downcast to a non-ancestor class.
- A fateful occurrence cannot reasonably be prevented.
- Writing to a full disk, accessing a missing web server.
Handling Occurrences
- There is no good excuse for encountering an avoidable occurrence.
- It results from ignorance, indolence, or incompetence.
- There is not good protection against encountering a fateful occurrence.
- Protection against fate is costly verses the benefit gained.
Checked vs. Unchecked Exceptions
- Java uses checked exceptions to “help” with fateful occurrences.
- A checked exception must be explicitly announced as a
possibility.
- An unchecked exception requires no such announcement.
- Exception and all ancestors (except Runtime) are checked.
- Runtime and Error exceptions are unchecked.
The throws Clause
- A method announces a checked exception via a throws clause:
throws ex [ , ex ]...
- A throws clause appears after the method’s signature
String read() throws IOException { ... } - A method propagating an unlisted checked exception causes a compile-time error.
Inheritance and throws
- A child method overriding a parent method cannot throw more exceptions
than the parent method does.
- It may throw fewer; it may throw none.
- The child exception types thrown must be descendants of the parent exception types.
- The
throwsclause doesn’t take part in determining the override.
Example
class RedException extends Exception { ... }
class BlueException extends Exception { ... }
class p
int moo() throws RedException { ... }
class c1 extends p
int moo()
throws RedException, BlueException { ... }
class c2 extends p
int moo() throws Exception { ... }
class c3 extends p
int moo() { ... }
Javadoc and Exceptions
- List exceptions in Javadoc with the
@throwstag. - List checked exceptions in Javadoc as well as in throws clauses.
- Document unchecked exceptions only in Javadoc.
- Throws clauses are scary (because of the responsibilities),
big throws classes are even scarier,
unnecessarily big throws clauses are annoying.
- Throws clauses are scary (because of the responsibilities),
Defining Exceptions
- Reasonably involved packages should define an exception set if
applicable.
- Classes that have their own exception set are probably too big.
- Determine if the exception set is checked or unchecked (or both, which is a pain).
- Extend the most distant ancestor of Exception that seems appropriate.
Exception-Defining Tips
- Use existing exceptions if possible.
- Go easy on the checked exceptions.
- And don’t freak on the taxonomy.
- Define leaf exceptions for throwing; parent exceptions for extending.
Exceptional Exceptions
- Exceptions are expensive and obscure.
- Unwinding the stack is disruptive.
- Exceptions start down there, wind through here, and may go up there.
- Exceptions should be mark rare, unusual, and significant events.
- Avoid using exceptions for run-of-the-mill control and communication.
Example
- Loops are optimized; exceptions are not.
-
f()’s exceptions are masked.- Selective catch clauses don’t help.
- Control is quickly obscured with more code.
- However, some thoughtfully disagree.
|
|
Runtime Exceptions
- Do not ignore runtime exceptions.
- Your code’s doing something wrong; fix it.
- This is particularly true for null-pointer access and array-index errors.
- Runtime exceptions may occur at the edges of your code.
- Where your code rubs up against not-your code.
Example
- The problem.
Exceptions thrown during execution (count exception): 360 java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException 1771 java.lang.NullPointerException 36 java.lang.RuntimeException- The cause.
// TODO REMOVE ALL STACK TRACES!!!! catch(StringIndexOutOfBoundsException f) { } catch(NullPointerException f) { } - The cause.
Summary
- Consider alternative, non-exception error-handling techniques.
- Use exceptions in exceptional, potentially troublesome circumstances.
- Document exception use.
Credits
- Black Swan by davesag under an AT, NC, SA Creative Commons license.