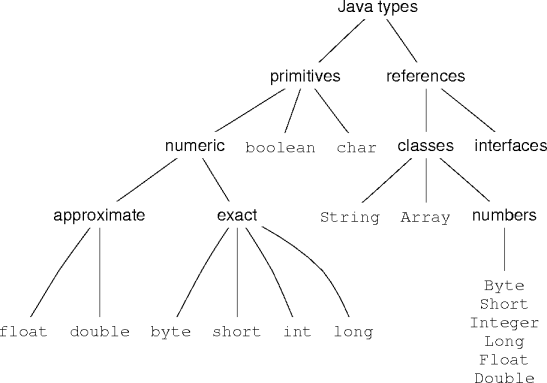

true and false.
'a'), Unicode
escapes ('\uxxxx'), and a small set of letter
escapes ('\t').
Name n literal byte8 1short16 -1int32 0long64 0Lor0l
float) or 64-bit
(double) IEEE-754 floating-point numbers.
float literals end in f or F; double literals end
in an optional d or D.
1f,3.14,-0.271e+1D
|
|
|
| target type | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
byte |
char |
short |
int |
long |
float |
double |
|
byte |
|||||||
char |
|||||||
short |
|||||||
int |
|||||||
long |
|||||||
float |
|||||||
double |
|||||||
| : Compatible. | t = s |
|
| : Cast required (with possible loss). | t = (t) s |
|
| : Compatible with possible loss. | t = s |
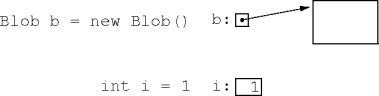
void m() {
Object o = 42;
}
java.lang.Number children.
void m() {
Object o = new Integer(42);
}
primitive-typeValue() in java.lang.Number.
void m(String key) {
if (hashTable.containsKey(key))
int i =
((Integer) hashTable(key)).intValue();
}
void m() {
Object o = 42;
}
void m(String key) {
if (hashTable.containsKey(key))
int i = hashTable(key);
}
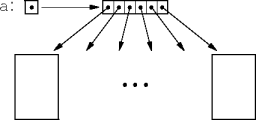
[] access operator.
a referencing an array of elements of type T has
the declaration
T[] aor Ta[]
T[][] aor Ta[][][]
int [] ia = new int [10];char ttt[][] = new char [3][3];
StringBuffer segs[] =
{ new StringBuffer(),
new StringBuffer(),
new StringBuffer() };
char ttt[][] = {
{ ' ', 'x', 'o' },
{ ' ', 'x', 'o' },
{ 'x', 'o', ' ' } };
int p[] = int [] { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 };
[] initializer is a convenient way to
construct an anonymous array.
t.sum(int [] { 1, 2, 3 });
point []
getOutliers(double mean, double stdDev) {
/* blah blah blah */
}
result = data.getOutliers(m, sd)
if (result != null)
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++)
// blah blah blah
result = data.getOutliers(m, sd) for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) // blah blah blah
[]).
String methods.
char.
s1 and s2 are strings, what does s1 == s2 do?
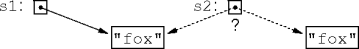
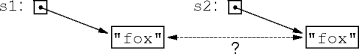
s1.equals(s2) do?
StringBuffers over Strings for manipulating strings.
s += "!" for string s.
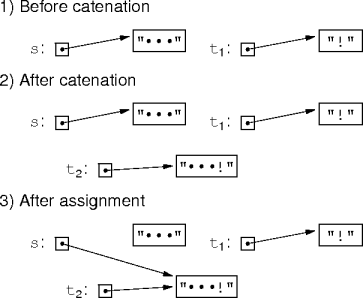
sb.append("!") for string buffer sb.
do ??? while not in.eof
s += in.read()1.1 sec. sb.apend(in.read())0.17 sec.
toString() MethodString toString() returns a printable
representation of a class instance.
Object, not from String.
toString() for significant classes.
employeeName.toString()→
"EmployeeName@1cd2e5f", not so good.
employeeName.toString()→
"George Leroy Tirebiter", better.
toString) and 27 (Return zero-length
arrays, not nulls) from Effective Java by Joshua Bloch, Addison-Wesley,
2001.