Outline
- I-O varities.
- Binary Stream I-O.
- Text Readers and Writers.
- Linking Text and Binary I-O.
|

|
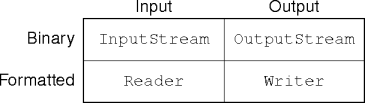
Binary vs. Formatted I-O
- Ultimately, all I-O is in bits (or bytes).
- Binary I-O leaves these bytes uninterpreted.
- And unstructured beyond byte sequences.
- Formatted I-O interprets the bytes involved.
- “Formatted” implies a textual structure.
- Record I-O implies different structures and interpretations.
3-Axis I-O
- There's three ways of looking at I-O:
- Binary vs. formatted (machine vs. humans).
- Unstructured vs. structured (bit streams vs. records).
- Uninterpreted vs. interpreted (formatting).
- Unfortunately, these are not independent axes.
- Interpretation (usually) requires structure.
Abstract Input and Output
-
InputStream and OutputStream are the
abstract ancestors of all I-O streams.
- Prefer the most abstract representation of a stream class.
Output Streams
void close()
void flush()
- Make sure output clears the pipe.
abstract void write(int b)
- Write the rightmost (least significant) byte.
void write(byte [] b)
void write(byte [] b, int off, int len)
Input Streams
int available()
- A guess at the available byte count.
void close()
long skip(long n)
- Skip bytes; return the count of bytes skipped.
Reading Input Streams
abstract int read()
- Return the next byte read or -1 if there won't be any more.
- Blocks if no bytes are available but more may come.
int read(byte [] b)
int read(byte [] b, int off, int len)
- Returns the number of bytes read or -1.
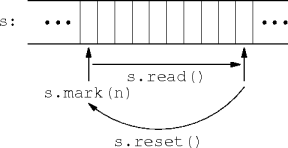
Marking Input Streams
Less Abstract I-O Streams
- From where to the bytes come? And to where do they go?
- Concrete classes associated with byte sources and sinks.
- Some byte sources and sinks have capabilities in advance of those
provided by
Input- and OutputStreams.
Input-Stream Classes
-
ByteArrayInputStream: read bytes from an array.
ByteArrayInputStream(byte [] buff)
-
FileInputStream: read bytes from a file.
FileInputStream(File file)
FileInputStream(String name)
-
AudioInputStream: read encoded audio frames.
AudioInputStream(InputStream is,
AudioFormat fmt, long len)
Output-Stream Classes
-
ByteArrayOutputStream: write bytes to an array.
ByteArrayOutputStream()
-
FileOutputStream: write bytes to a file.
FileOutputStream(File file)
FileOutputStream(
File file, boolean append)
FileOutputStream(String name)
FileOutputStream(
String name, boolean append)
Stream Capabilities
- Some stream sources and sinks have special capabiblites.
- Disk files have efficient random access.
- Network connections have piecemeal transmission.
- Some streams contents have special capabilities.
- It may be encrypted or compressed.
- Filter streams deal with stream capabilities.
Filter Streams
- Transport

- Transformation
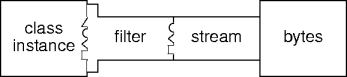
- And so on, and so on.
Input Filters
Input-Filter Example
import javax.crypto.CipherInputStream;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
void seekritRead(String filename, Cipher cipher)
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
final InputStream inputStream =
new CipherInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(filename)),
cipher);
// blah blah blah
inputStream.close();
}
Output Filters
I-O Stream Summary
- There are three levels to the I-O stream hierarchy:
- Abstract input and output streams.
- Concrete (usually) source or sink streams.
- Filter streams provided capabilities.
- Usable I-O streams are composed from source or sink streams and
filters.
- All treated as abstract input or output streams.
Data I-O
- Doing byte-oriented I-O is necessary, but inconvenient.
- How are Java primitive values input and output?
- The JVM makes binary I-O for primitive values useful.
- Fast, compact, and portable.
- The data I-O streams provide binary I-O for primitive values.
Data I-O
- The primitive types are
boolean, byte, short, char, int, long,
float, and double.
- There are read and write routines for each primitive.
writeBoolean(boolean)(), writeByte(), …
readBoolean(), readByte(),
…
- See the
DataInput and DataOutput
interface documentation for details.
Data I-O streams
-
DataInputStream and DataOutputStream
implement the Data I-O interfaces.
- These are filter streams.
final DataOutputStream outputStream =
new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(filename)))
outputStream.writeLong(checksum)
Human-Oriented I-O
- The stream class deals with bytes as bytes.
- Good for machines, bad for humans.
- Textual I-O, human oriented I-O, is handled by another set of classes.
- Textual I-O is also useful for machine-machine communication.
Abstract Readers and Writers
-
Reader and Writer are the abstract
ancestors of text-based I-O streams.
- As always, prefer Reader and Writer values where possible.
Writers
- The Writer abstract class deinfes the expected methods:
void close()
void flush()
- Make sure output clears the pipe.
void write(int c)
void write(char [] b)
void write(string s)
Writer Sinks
Readers
- The Reader abstract class defines a handful of the expected methods.
void mark(int n)
void reset()
int read()
int read(char[] cbuf)
abstract int read(
char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
- Other classes have to pick up the slack.
Reader Sources
Formatted Translation
-
PrintWriter translates binary values to a textual representation.
- Where's the reverse translation?
- It's not in the reader hierarchy.
- Prior to Java 5, text-to-binary translation was ugly.
- Since Java 5, the Scanner class makes it less so.
The Scanner
- The
Scanner class provides a simple text parser and
translator.
- Constructors and methods include
Scanner(Reader source)
double nextDouble()
short nextShort(int radix)
String nextLine()
- See the Scanner API documentation for details.
Character Sets
- Inside Java, characters are 16-bit Unicode code units.
- Outside of Java, they aren't.
- And they aren't in many different ways.
- The
Charset class is responsible for the translation
between encodings.
static SortedMap availableCharsets()
static Charset forName(String name)
ByteBuffer encode(String str)
CharBuffer decode(ByteBuffer buffer)
Reader-Writer Summary
- Reader and Writer hierarchies echo the I-O stream hierarchy.
- Readers and writers do character-set translation.
- Writers have extensive but simple binary-to-text translation.
- Readers rely on other classes for text-to-binary translations.
I-O Exceptions
- I-O Exceptions are checked exceptions.
- Propigated I-O exceptions must be declared in a throws clause.
- Or handled in the method or exception.
- Throw the most specific exception possible.
- With helpful extra information.
Summary
- I-O is a 2x2 matrix: (input, output) x (binary, formatted).
- Each matrix cell has three layers: abstract class, sources and sinks,
and filters.
- Assemble usable I-O abstractions by layering filters over sources and
sinks.
- For formatted I-O, look to other classes outside the I-O hierarchy.
- Particularly for reading.
Credits
|
This page last modified on 4 March 2008.
|

|