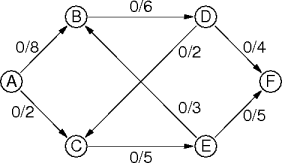

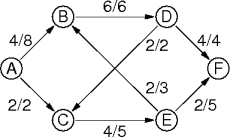
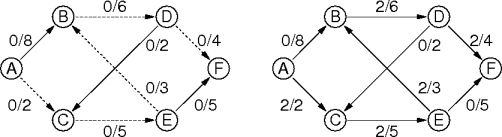
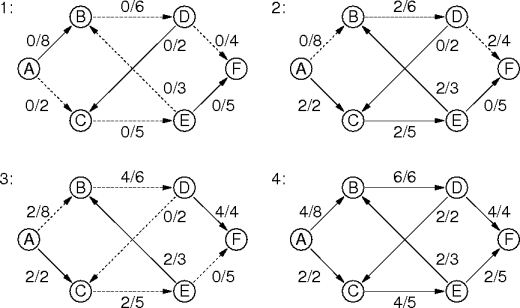
|
|
|

|
|
|
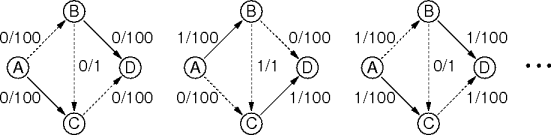
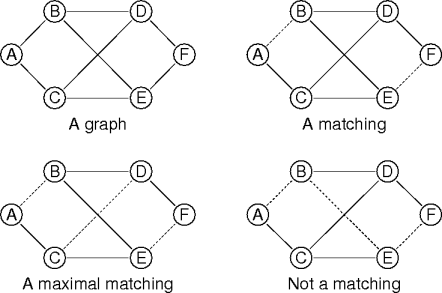
EM ⊆ EG and 2|EM| = |VM|That is, every vertex in M is adjacent to exactly one other vertex.
|
|
|
|
|
|
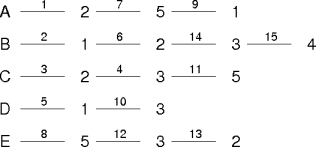
A: 2 5 1 3 4 B: 1 2 3 4 5 C: 2 3 5 4 1 D: 1 3 2 4 5 E: 5 3 2 1 4
1: E A D B C 2: D E B A C 3: A D B C E 4: C B D A E 5: D B C E A
A: 7 1 2 B: 4 2 1
1: F A B 2: E B A
A: 7 1 2 B: 4 2 1
1: F A B 2: E B A
|
|
|
|
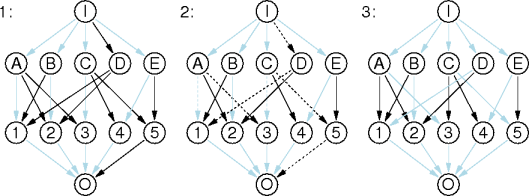
preferences with a row per hospital.
student with an element per hospital.
preferences[h,student[h]] is hospital h's current pairing.
preferences[h,++student[h]] is the next one.
rank with a row per student indexed by hospital.
hospital with an element per student.
s accept hospital h?
rank[s,h] > rank[s,hospital[s]]
n hospitals.
for h' = 1 to n
h = h'
do
student[h]++
s = preferences[h, student[h]]
if rank[s, h] > rank[s, hospital[s]]
swap(hospital[s], h)
while h > 0
s's more preferred hospitals are paired
with students they prefer more than s.
bool
grand_tour(graph g, vertex v, int l)
if l == g.vertices().size()
return true
v.visited = true
for n in g.neighbors(v)
if not n.visited
if grand_tour(g, n, l + 1)
return true
v.visited = false
return false
grand_tour(), in the worst case, explores every possible path.