Outline
- Background
- The problem.
- A solution.
- Testing
- Results
- Coding observations.
The Problem
- Read in a circuit description.
- Read in a sequence of circuit inputs.
- For each circuit input read, analyze the circuit and
- Print the maximum delay through the circuit.
- Print the circuit outputs.
A Solution
main()
const circuit c =
input_circuit(std::cin)
circuit_inputs ci;
while (input_inputs(std::cin, ci))
output_results(
std::cout, analyze(c, ci, emsg))
Wish List
- Data structures:
circuit
circuit-inputs
analysis-results
- Procedures:
input-circuit()
input-inputs()
analyze()
output_results()
What's Next?
- I-O is straightforward.
- How to do circuit analysis?
- How to find the maximum delay.
- How to compute outputs from inputs.
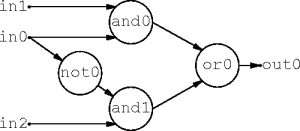
PERT Charts
- A circuit can be modeled by a PERT chart.
- Each component is a task.
- Each component needs all its inputs before it can produce an output.
- The component delay is the task duration.
- Circuit analysis reduces to PERT-chart analysis.
- A task schedule computes the outputs.
- The critical path is the maximum delay.
Maximum Delay
- A max-path algorithm finds the maximum delay.
- Modify the min-path algorithm by
- Replacing a min-heap with a max heap.
- Subtracting each weight from a large value (e.g. 2|V|).
- Using negative weights -w.
Output Values
- Find the reverse depth-first search path.
- Run down the path, using previously assigned component values to
compute the current component value.

in0 in1 in2 and0 not0 and1 or1 out0
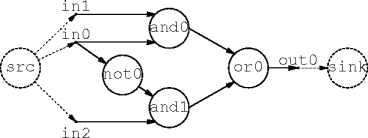
A Small Trick
- It is convenient to add source and sink vertices to the circuit.
Data Structures
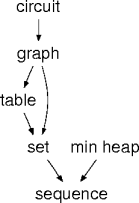
- The parent is the client; the child is the ADT.
Circuit Interface
// Add the given edge to the this graph.
void add-edge(from, to, err)
// Create a new, empty circuit.
circuit();
// Return this circuit's maximum delay.
unsigned maximum-delay() const
// Trace the inputs through this circuit,
// return the outputs.
circuit-inputs trace(inputs) const;
Circuit Private Data
graph g;
graph::vertex-label-set
input-ports, output-ports;
mutable int max-delay;
mutable sequence<graph::vertex-label-type>
schedule;
static const graph::vertex-label-type
source-node, sink-node;
Graph Interface
typedef std::string vertex_label_type;
typedef set<vertex_label_type>
vertex_label_set
void add_edge(from, to, err)
vertex_label_set
incoming_nodes(label) const
vertex_label_set
outgoing_nodes(label) const
const vertex_label_set &
vertices() const
Graph Private Data
table<vertex-label-type,
sequence<vertex-label-type>
incoming, outgoing
vertex-label-set nodes
vertex-label-set
graph::incoming_nodes(
const vertex-label-type & label)
return incoming.get(label)
Testing
- Garbage and empty tests.
- Component node tests.
- Three-majority test.
- Half-adder test.
- Corner cases: bad nodes, mis-configured nodes, and so on.
Results
| Tests |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
| 1 |
| | | | | | | | | |
| 2 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Know Your Tools.
int checkForBlankLine(string inputLine)
int spaces = 0
while (spaces < inputLine.length()) and
isspace(inputLine[spaces])
spaces++
if spaces == inputLine.length()
return -1
return spaces++
Know Your Tools..
int checkForBlankLine(string inputLine)
const unsigned n =
inputLine.find_first_not_of(" \n\t");
return n == string::npos ? -1 : n;
- It's called a language because everybody understands it.
- You should understand it too.
- Speak in a common tongue.
Avoid Public ADT Data
struct Circuit_or_Port
Circuit_or_Port(const Circuit_or_Port &)
~Circuit_or_Port()
void operator =(const Circuit_or_Port &)
void addAjacentLabel(adjacentLabel * &)
void addComponent(Circuit_or_Port * &)
string circuitOrPortType
int propagationTime
bool visited
int receivedInputs
int valueOfInputs
int valueOfOutputs
int noOfInputWires
int noOfOutputWires
int currentInputWireArraySize
int currentOutputWireArraySize
int* inputWires
string* receivedFrom
adjacentLabel * adjacentVertex
Circuit_or_Port * nextVertex
Expose ADT Methods
struct graph
public:
graph()
graph(const graph& agraph)
~graph()
void operator = (const graph & agraph)
gate* addgate(string, string)
gate* addgate(string, string, gate *)
gate* getgate(int index)
int getsize()
int getisize()
int getosize()
gate* gatesearch(string aname)
void addin(gate*)
void addout(gate*)
void init(int thesize)
bool eval(bool ins[], bool outs[], int& del)
void reset()
void pprint()
Keep ADT Data Hidden
- Public ADT Data is
- Hard to change.
- Clients have to change along with the data.
- Hard to keep correct.
- Clients can muck with the data any way they want.




