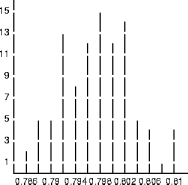
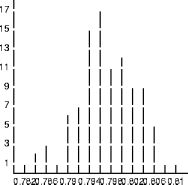
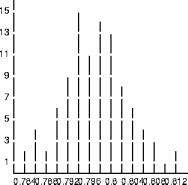
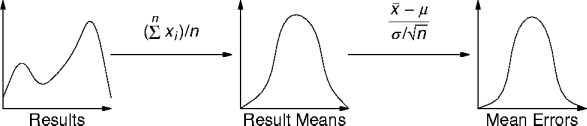
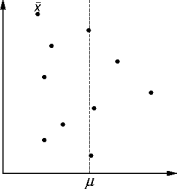
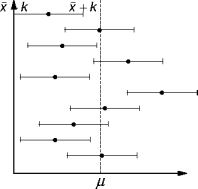
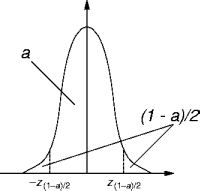
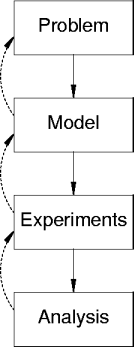
- Overall, a simulation has four phases:
- Understand the problem to extract a system.
- Abstract the system as a model.
- Experiment with the model.
- Design the experiments.
- Run the experiments.
- Analyze the experiment results.
- Each phase has sub-phases, including be validation and verification.
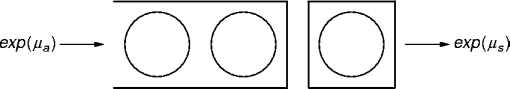 find the server utilization (server busy/total time).
find the server utilization (server busy/total time).