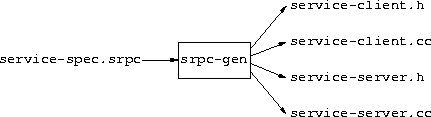
The sRPC types are bound to the analogous types in C++:
| sRPC type | Bound C++ type |
|---|---|
int | int |
string | std::string |
array of T | std::vector<T> |
Each service call is bound to a prototype of the form
void call-name(input-parameters,output-parametersThe left-to-right order of the input parameters matches the top-to-bottom order of the in-parameter specs in the service-spec; similarly for the output parameters. An input-parameter spec
in type-spec ident
is bound to the formal parameter
const bound-type-spec & ident
or to
depending on the parameter type. An output-parameter spec
out type-spec ident
is bound to the formal parameter
& ident
As an example, the Dictionary service-call spec tableau_scs() is bound to the prototype
void insert( const std::string & word, int & inserted, std::string & emsg )
The client-side generic sRPC service calls have the bindings
service-name( const std::string & hostname, short port_number, std::string & emsg ) void query( std::string & spec, std::string & emsg ) void shutdown( std::string & emsg )
The setup generic sRPC service call becomes the class's constructor, but the shutdown generic sRPC service call does not become the class's destructor (although the destructor may call fun(shutdown) if it needs to).
On the server side, the service-call specs and server-specific generic sRPC service calls are bound to procedures in a namespace with the same name as the service.
srpc-gen creates four C++ source files from a
service-spec file:
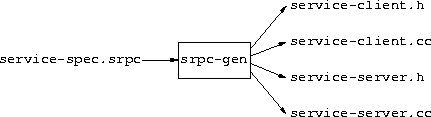
The client.h file contains the declarations of the client-side interface
routines defined in the client.cc file. Any implementer-supplied
client-side code that make service calls needs to include the clients.h
file.
The client.cc file contains the definitions of the client-side interface
routines for the service. The implementer compiles and links this file with
the client-side code.
The server.h file contains the declarations of the server-side interface
routines called in the server.cc file. The server-side code implementing
service calls needs to include the server.h file.
The server.cc file lets the sRPC server-side run-time system call-out to
the implementor-supplied code for the service. The implementer compiles and
links this file with the server-side code.
This page last modified on 29 March 2004.