- List behavior.
- The list class.
- Constructors
- Growing and shrinking lists.
- Inserting and removing list elements.
- Splicing
- List relations.
- Iterators and value access.
- List member functions.
- Lists are a sequential data type, but not like arrays or
vectors.
- Lists do not have indexed access via
[] or at().
- Lists have uniform, efficient insert and delete operations.
- Efficient inserts and deletes can happen anywhere in a list.
- Lists have good invalidation behavior.
- Lists have restricted iterators; no jumping.
- Lists are doubly-linked; traversals cost the same in
either direction.
- Lists are not circular; they have two ends.
- Defined in the
<list> header.
- The single template parameter gives the list-element
type.
- Forgetting, as always, the allocator template
parameter.
- The list class has a number of list-specific member
functions.
- They make up for the weaker list iterators.
- The default constructor
list<T> l.
- The size and value constructor
list<T> l(n, v).
-
v is optional with a T default constructor.
- The copy constructor
list<T> l2(l1).
-
l1 list elements are copied into l2, not shared with
l2.
- The iterator-range constructor
list<T> l(start, end).
- The
start and end iterators can point into
any container, not just a list.
- The elements are copied into
l, not shared with l.
- No element access via
[] or .at().
- Iterator access as always.
- First and last element access via
front() and
back().
-
size() and max_size() member functions.
- No
reserve() and capacity() member functions.
-
l.push_back(v), l.pop_back(),
l.push_front(v), and l.pop_front() member
functions.
-
l.resize(n) changes the number of elements in l to n.
- This may add or remove elements at the end of the list.
- Default values are added if necessary.
-
l.resize(n, v) changes the number of elements in l to n.
- This may add or remove elements at the end of the list.
- Copies of the value
v are added if necessary.
-
insert(i, v) inserts the value v immediately
before (to the left of) the value referenced by the
iterator i.
-
insert(i, n, v) inserts n copies of the
value v immediately before (just to the left of)
the value referenced by the iterator i
-
insert(i, start, end) inserts the values denoted
by the iterator range start,end immediately
before the value referenced by the iterator i.
- None of these operations invalidate iterators.
-
erase(i) deletes the value referenced by the
iterator i.
-
erase(s, e) deletes the values denoted by the
iterator range (s, e)
- Both return an iterator to the next (to the right)
element.
-
remove(val) removes all elements with the given
value.
-
remove_if(p) removes all elements for which p()
returns true.
-
clear() removes all elements.
- Only iterators referencing deleted elements are
invalidated.
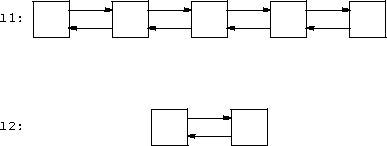
- Splicing is a form of insertion available only to lists.
-
List splicing moves a chunk of one list to another list.
-
l1.splice(i, l2) inserts the list l2 before
the list l1 value referenced by iterator i.
-
l2 is empty after the splice.
-
l1 and l2 must be different.
-
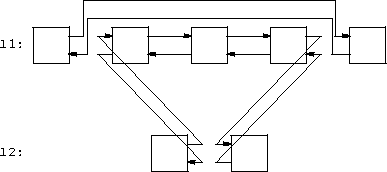
l1.splice(i1, l2, i2) inserts the l2 value
referenced by the iterator i2 before the list
l1 value referenced by iterator i1.
- The value referenced by
i2 is deleted from
l2.
-
l1 and l2 need not be different.
-
l1.splice(i1, l2, 2, e) inserts the l2 values
referenced by the iterator range (s, e) before the
list l1 value referenced by iterator i1.
- The values referenced by
(s, e) are deleted from
l2.
-
l1 and l2 need not be different, but the
iterator range may not contain i1.
- These operations
invalidate no iterators
and take constant time.
- The usual types
- List iterators are bidirectional iterators
- no jumping around via
+, -, +=, or
-=.
- No distance measurement via
-.
- No relations other than equality.
- Some generic algorithms don't work on lists.
- The usual member functions
- List member functions make up for the loss of generic
algorithms.
- Most are faster than the corresponding generic
algorithm.
- Pointer moving rather than data moving.
-
l.sort() sorts l in O(n2) time.
-
l.sort(c) sorts l using the comparison c.
-
unique() replaces consecutive runs of a value with
one copy of the value.
-
unique(p) replaces consecutive runs with a single
value using p to determine when adjacent values are
equal
-
l1.merge(l2), l1.merge(l2, c) merges l2
into l1, using c; l2 is empty after.
- Both
l1 and l2 should be sorted; the merged
list is sorted too.
|
vector | list |
|---|
| insert and erase |
O(n) | O(1) |
push_front() |
O(n)1 | O(1) |
find()3 |
O(n) | O(n) |
| C[i] |
O(1) | O(n)2 |
| iterator |
random | bidirectional |
- Notes
- Vectors don't implement
v.push_front(X); v.insert(v.begin(),
X) is the equivalent.
- Lists don't implement
operator []; std::advance(l.begin(),
i) is the equivalent.
-
std::find() is a generic algorithm not re-implemented by either
vectors or lists.
|
vector |
list |
|---|
c.insert(i, v) |
j >= i, possibly all |
none |
c.erase(i) |
j >= i |
i |
c.push_back(v) |
c.end(), possibly all |
none |
c.pop_back() |
--c.end(), c.end() |
--c.end() |
c.push_front(v) |
all1 |
c.begin() |
c.pop_front() |
all2 |
c.begin() |
- Notes
- Vectors don't implement
v.push_front(X); v.insert(v.begin(),
X) is the equivalent.
- Vectors don't implement
pop_front(); v.erase(v.begin())
is the equivalent.
- Slists (singly-linked lists) are a non-standard extension to the STL.
- They have been proposed as an addition to the standard.
- They are smaller and faster than doubly-linked lists.
- Less data and operational overhead.
- Slists have forward iterators.
- Inserting is an interesting problem for lists.
- Values are inserted before the associated iterator.
- Insertion costs are O(n).
- The
.insert_after() member functions are O(1) iterators.
- Lists are doubly-linked lists.
- Lists support several unique member functions.
- Including
.splice(), .remove(), .unique(), .merge(), and
.sort().
- Lists vs. vectors.
- Invalidation behavior is the clincher.
- Slists are a non-standard extension to the STL.
This page last modified on 24 February 2004.