- A stream may contain an arbitrary number of elements.
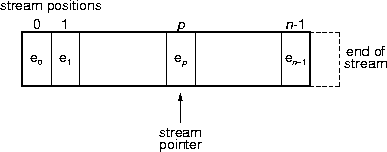
- Stream position
- Stream pointer
- Stream data elements
- The stream ends.
- The end-of-stream (or eos) position.
stdio library.
stdio in C.

char and wchar_t.
char | wchar_t | |
| input | <istream> | <wistream> |
| output | <ostream> | <wostream> |
| both | <iostream> | <wiostream> |
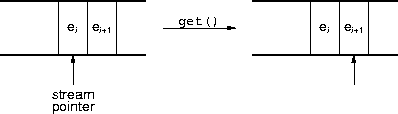
istream & istream::get(char & c) istream & istream::getline( char * str, streamsize cnt) istream & istream::ignore() istream & istream::unget() streamsize istream::gcount()

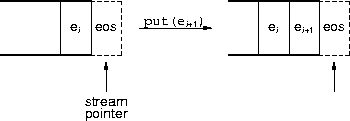
ostream & put(char c) ostream & write( const char * s, streamsize cnt) ostream & flush()
good(), fail(), bad(), and eof().
fail() tests for the fail or bad states.
clear()ed.
| Don't do this | Do this |
| while true cin >> x if cin.eof() break // whatever |
! tests a stream's fail or bad
state.
!cin is the same as cin.fail().
std::ofstream of(filename) if (!of) // Can't open the file.
! does not test the stream's end-of-stream state.
void * pointers.
void * pointers convert to a boolean value.
cin.fail() is false,cin converts to a non-null void * converts to true.
cin.fail() is true, cin converts to a null void * converts to false.
-?[0-9]+.
1; false has format 0.
>> performs
formatted input from a stream.
istream >> variable
<< performs formatted
output to a stream.
ostream << value
istream >> x >> y ostream << "y = " << y << "\n"
endl and perhaps the flush
manipulators.
hex manipulator sets the base to hexadecimal.
std::cout << 18 << std::hex << ' '
<< 19 << ' ' << 20
produces
18 13 14
setw() manipulator sets the field width for the next value
read or written.
cout << 3 << std::setw(4) << 4 << 5
produces
3 45
.close() member function dis-associates a stream from a file.
.is_open() member predicate determines if an association
exists.
fs.open(fname) associates file stream fs and
the file with the name fname using the default modes.
fs.open(fname, modes) uses the modes
modes instead of the default modes.
in | open for reading |
out | open for writing |
app | writes append |
ate | start at the eos position |
trunc | empty the file |
binary | do not modify characters |
istringstream.
ostringstream.
stringstream.
<sstream>.
<strstream>; it's deprecated.
ss.str() member function returns the string associated with the
string stream ss.
ss.str(str) member function sets the string
associated with the string stream ss to the string str.
istringstream is("hello");
is the same as
istringstream is;
is.str("hello");
tellp() for write pointers and tellg() for read pointers.
seekp() for write pointers and seekg() for read pointers.
This page last modified on 6 May 2004.