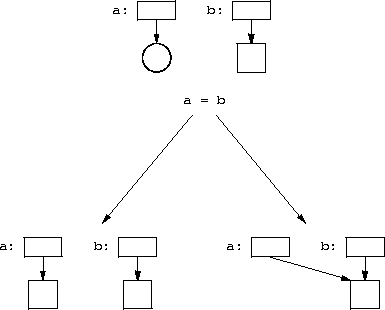

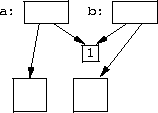
handle<widget> wh1(blue) handle<widget> wh2(wh1) wh2->color = red // Now wh1->color is red too.
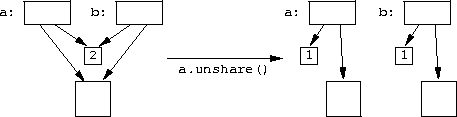
unshare() member function copies storage.
template < typename T >
void handle::unshare()
if (*ref_cnt > 1)
(*ref_cnt)--
ref_cnt = new size_t(1)
t_ptr = t_ptr->clone()
clone() operation.
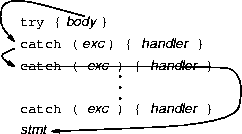
or be unwound.
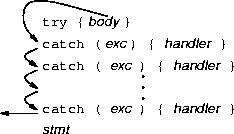
unshare() and Exception Safetyunshare() exception safe?
if (*ref_cnt > 1) 1 (*ref_cnt)-- 2 ref_cnt = new size_t(1) 3 t_ptr = t_ptr->clone()
(*ref_cnt)--.
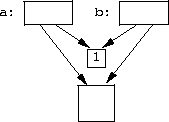
ref_cnt = new size_t(1).
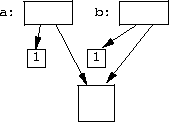
t_ptr->clone() throws an exception.
unshare() Exception Safeif (*ref_cnt > 1) t_ptr = t_ptr->clone() (*ref_cnt)-- ref_cnt = new size_t(1)
unshare() exception safe?
new size_t(1) throws an exception.
if (*ref_cnt > 1) T * tp = t_ptr->clone() size_t * rcp = new size_t(1) (*ref_cnt)-- ref_cnt = rcp t_ptr = tp
unshare() Really Exception Safeunshare() exception safe yet?
if (*ref_cnt > 1) T * tp = t_ptr->clone() size_t * rcp = new size_t(1) (*ref_cnt)-- ref_cnt = rcp t_ptr = tp
new size_t(1) throws an exception?
if (*ref_cnt > 1)
T * const tp = t_ptr->clone()
size_t * rcp
try { rcp = new size_t(1) }
catch (...) { delete tp ; throw }
(*ref_cnt)--
ref_cnt = rcp
t_ptr = tp
unshare() fixed, are handles exception safe?
template < typename T > handle::handle(T * tp) : ref_cnt(new size_t(1)), t_ptr(tp) { }
handle<widget> wh(new widget)
new size_t(1) throws, new widget is lost.
widget * wp = new widget
handle<widget> wh
try { wh = handle<widget>(wp) }
catch (...) { delete wp ; throw }
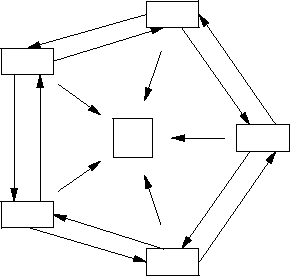
template < typename T >
class handle
public:
handle()
: tptr(0), next(this), last(this) { }
handle(T * tp)
: tptr(tp), next(this), last(this) { }
private:
T * tptr
mutable handle * next, * last
handle(const handle & h) { relink(h) }
handle & operator = (const handle & rhs)
if (this != &rhs)
unlink()
relink(rhs)
return *this
~handle()
unlink()
void unlink()
if next == last
delete tptr
else
next->last = last
last->next = next
void relink(handle & h)
next = &h
last = h.last
h.last = last->next = this
tptr = h.tptr
const not const?handle & operator = (const handle & rhs)
rhs is logically but not actually const.
handle & operator = (const handle & rhs)
if this != &rhs
// whatever
const_cast<handle &>(rhs).last = this
mutable vs. constmutable modifier was defined to avoid these problems.
mutable handle * last, * next
handle & operator = (const handle & rhs)
if this != &rhs
// whatever
rhs.last = this
These notes were derived from this article.
Smart Pointers Reloaded (IV): Finale by Andrei Alexandrescu and David Held, C/C++ Users Journal, April, 2004.
Combines reference counting and circular pointers to minimize heap-access overhead.
This page last modified on 6 May 2004.