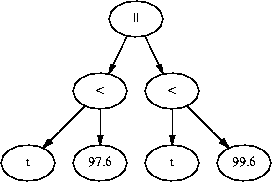
(t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t).
template <class Temps>
unsigned abnormal_count(const Temps & temps)
return
std::count_if(
temps.begin(), temps.end(),
abnormal_temperature)
static bool
abnormal_temperature(double temp)
return (temp < 97.6) or (99.6 < temp)
template <class Temps>
unsigned normal_count(const Temps & temps)
return
std::count_if(
temps.begin(), temps.end(),
std::not1(
std::ptr_fun(
abnormal_temperature)))
template <class Temps>
unsigned abnormal_count(const Temps & temps)
return std::count_if(
temps.begin(), temps.end(),
abnormal_temperature
t < 97.6 || 99.6 > t)
? 1 + 3 4 ? (10 + 13 + 8)/3 10.33 ?

(t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t).

typedef double result_type
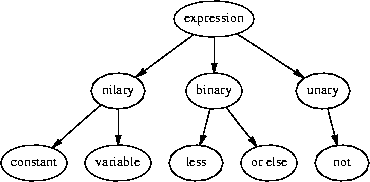
class expression
public:
virtual result_type evaluate() const = 0
class nilary_expression : public expression
class unary_expression : public expression
protected:
expression * operand
class binary_expression : public expression
protected:
expression * left, * right
struct literal : public nilary_expression
literal(result_type v) : value(v) { }
result_type evaluate() const
return value
private:
result_type value
struct less : public binary_expression
less(expression * l, expression * r)
left = l
right = r
result_type evaluate() const
return
left->evaluate() < right->evaluate()
$ cat ex-test.cc
#include <iostream>
#include "expression.h"
int main()
double t = 102.3
// t < 97.6 || 99.6 < t
expression * ep =
new or_else(
new less (
new variable(t), new literal(97.6)),
new less (
new new literal(99.6), variable(t)))
std::cout
<< t << " is "
<< (ep->evaluate() ? "ab" : "")
<< "normal.\n"
$ g++ -o ex-test ex-test.cc
$ ./ex-test
102.3 is abnormal
$
See the complete code.
result_type or_else::
evaluate() const
return
left->evaluate() || right->evaluate()
result_type sum::
evaluate() const
return
left->evaluate() + right->evaluate()
result_type xor::
evaluate() const
return
left->evaluate() ^ right->evaluate()
left could be a binary expression or a literal.
template
<class LExpr, // Left operand's type.
class RExpr, // Right operand's type.
class BinOp> // Binary operator's type.
struct binary_expression
binary_expression(
LExpr l, RExpr r, BinOp op = BinOp())
: left(l), right(r), op(op) { }
result_type evaluate() const
return
op(left.evaluate(), right.evaluate())
private:
LExpr left
RExpr right
BinOp op
typedef double result_type
struct literal
literal(result_type v) : value(v) { }
result_type evaluate() const
return value
private:
result_type value
struct variable
variable(result_type & v) : var(v) { }
result_type evaluate() const
return var
private:
result_type var
$ cat et-test.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include "expression.h"
int
main()
result_type t = 102.5
// (t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t)
const bool abnormal =
binary_expression<
binary_expression
<variable, literal, std::less<result_type> >,
binary_expression
<literal, variable, std::less<result_type> >,
std::logical_or<result_type> >
(binary_expression
<variable, literal, std::less<result_type> >
(variable(t), literal(97.6)),
binary_expression
<literal, variable, std::less<result_type> >
(literal(99.6), variable(t))).evaluate()
std::cout
<< t << " is "
<< (abnormal ? "ab" : "")
<< "normal.\n"
(t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t).
binary_expression
<binary_expression
<variable, literal, std::less<rtype> >,
binary_expression
<literal, variable, std::less<rtype> >,
std::logical_or<result_type>
>
(binary_expression
<variable,
literal,
std::less<result_type>
>
(variable(t), literal(97.6)),
binary_expression
<literal,
variable,
std::less<result_type>
>
(literal(99.6), variable(t)
)
$ g++ -o et-test et-test.cc $ ./et-test 102.5 is abnormal. $ CC -o et-test et-test.cc $ ./et-test 102.5 is abnormal. $
evaluate()?
for this scheme to work well.
template <class LExpr, class RExpr>
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> >
make_less(LExpr l, RExpr r)
return
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> >
(l, r)
template
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::logical_or<rtype> >
make_logical_or(LExpr l, RExpr r)
return
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::logical_or<rtype> >
(l, r)
const bool abnormal =
make_logical_or(
make_less(variable(t), literal(97.6)),
make_less(literal(99.6), variable(t))
).evaluate()
make_less(variable(t), literal(97.6))
resolves to the template function
template <class LExpr, class RExpr>
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> >
make_less(LExpr l, RExpr r)
return
binary_expression
<LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> >
(l, r)
with LExpr binding to variable and RExpr binding to
literal.
template <class LExpr, class RExpr> binary_expression <LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> >make_less(LExpr l, RExpr r)operator < (LExpr l, RExpr r) return binary_expression <LExpr, RExpr, std::less<rtype> > (l, r) templatebinary_expression <LExpr, RExpr, std::logical_or<rtype> > make_logical_or(LExpr l, RExpr r)operator || (LExpr l, RExpr r) return binary_expression <LExpr, RExpr, std::logical_or<rtype> > (l, r)
const bool abnormal = ((variable(t) < literal(97.6)) || (literal(99.6) < variable(t))).evaluate()
variable() calls by delaring them before hand.
return_type temp = 100 variable t = temp const bool abnormal = ((t < literal(97.6)) || (literal(99.6) < t)).evaluate()
return_type temp = 100 variable t = temp const bool abnormal = ((t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t)).evaluate()
what is the type of t < 97.6?
binary_expression <variable, double, std::less<result_type> >
evaluate().
literal::literal(return_type v) is a cast conversion.
double -> literal
struct double_representation typedef literal type
double_representation::type
struct literal_representation typedef literal type struct variable_representation typedef variable type struct unary_expression_representation typedef unary_expression type struct binary_expression_representation typedef binary_expression type
template < class ExprType > struct representation typedef ExprType type
T is
representation<T>::type
and is the same as T.
template < > struct representation<int> typedef literal type template < > struct representation<double> typedef literal type // and so on for bool, short, ...
T is
representation<T>::type
and is the same as literal literal.
representation<double>::type
resolves to
template <class ValueType> struct representation typedef ValueType type
with ValueType as double, and to
template < > struct representation<double> typedef literal type
but the latter is more specific.
template
<class LExpr, // Left operand's type.
class RExpr, // Right operand's type.
class BinOp> // Binary operator's type.
struct binary_expression
binary_expression(
LExpr l, RExpr r, BinOp op = BinOp())
: left(l), right(r), op(op) { }
result_type evaluate() const
return
op(left.evaluate(), right.evaluate())
private:
LExpr left
typename
representation<LExpr>::type left
RExpr right
typename
representation<RExpr>::type right
BinOp op
t < 101.5
with t declared a variable.
binary_expression <variable, double, std::less<result_type> >
right has type
typename representation<RExpr>::type
RExpr is double, representationtemplate < > representation<double> typedef literal type
right has type literal.
right(r) converts the double 101.5 to the
literal right.
$ cat et-traits.cc
int
main()
result_type temp = 450.0
variable t = temp
const bool abnormal =
((t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t)).evaluate()
std::cout
<< temp << " is "
<< (abnormal ? "ab" : "")
<< "normal.\n"
$ g++ -o et-traits et-traits.cc
$ ./et-traits
450 is abnormal.
$
evaluate().
result_value literal::evaluate(result_value) return v
result_value variable::evaluate(result_value v)return varreturn v
result_value binary_expression::
evaluate(result_value v)
return
operator(
left.evaluate(), right.evaluate()
left.evaluate(v), right.evaluate(v))
$ cat et-lambda.cc
template < class Expression >
static result_type
find_max(Expression expr,
double l, double r, double s)
result_type mx = expr.evaluate(l)
while l < r
mx = std::max(expr.evaluate(l), mx)
l += s
return mx
int main()
variable x
std::cout
<< find_max((x - 3)*(x - 5), 1, 10, 1)
<< "\n"
<< find_max((x - 3)/(x + 5), 1, 10, 1)
<< "\n"
$ g++ -o et-lambda et-lambda.cc
$ ./et-lambda
24
0.428571
$
evaluate() into a call operator.
result_value
literal::operator () (result_value)
return v
result_value
variable::operator () (result_value v)
return v
result_value binary_expression::
operator () (result_value v)
return
op(left.evaluate(v), right.evaluate(v))
op(left(v), right(v))
$ cat et-callable.cc
template <class Temps>
static unsigned
abnormal_count(const Temps & temps)
variable t
return
std::count_if(
temps.begin(), temps.end(),
(t < 97.6) || (99.6 < t))
int main()
double temps[] =
{ 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101}
std::vector t(temps, temps + 7)
std::cout << abnormal_count(t)
<< " abnormal temperatures.\n"
$ g++ -o et-callable et-callable.cc
$ ./et-callable
5 abnormal temperatures.
$
These notes were derived from this article.
The Boost Lambda Library.
An industrial-strength implementation of the ideas discussed here.
This page last modified on 6 May 2004.