0 and contains only
octal numbers (0 through 7). A decimal number begins with 1
through 9 and contains only decimal digits. A hexadecimal number begins
with either 0x or 0X and contains only hexadecimal digits (0
through 9 and a through f in either case). A number should be
as long as possible.
Describe an algorithm that accepts a string and finds the first number in the string, or indicates that the string contains no number.
This recognizer accepts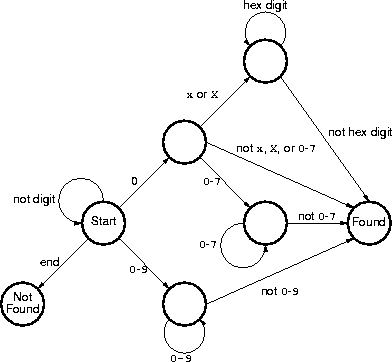
0x as a legal hex number, which it isn't.
However, the description didn't make this clear, so I accepted either
interpretation.
Given a multi-byte value, some CPU architectures store the most significant byte at the lowest address (the SPARC architecture, for example) while other CPU architectures store the least significant byte at the lowest address (the Intel architecture, for example).
A multi-byte value created on one architecture will be misinterpreted on the other architecture because the meaning assigned to the byte at the lowest address will be wrong: it will be the least significant byte interpreted as the most significant byte or vice versa. This is the byte-order problem.
The byte-order problem can be resolved by insuring multi-byte values are given some canonical external representation. Multi-byte values are read and written a byte at a time from most to least significant (or vice versa). With a canonical representation all bytes have the same order and everyone agrees (or at least knows of) the order.
int &) instead of an
integer pointer (int *) to return a value from a constructor.
- Integer references don't require the caller preceed the actual parameter
with an address-of operator
&. - When used as an optional formal parameter, an integer reference eliminates the need to check for a legitimate reference value, because the value is always legitimate.
a[i++] + a[i] can produce.
Let the value of i be i before evaluating the expression. If the
left-hand operand is evaluated first, the expression has the value
If the right-hand operand is evaluated first, the expression has the valuea[i] + a[i + 1]
a[i] + a[i]=2*a[i]