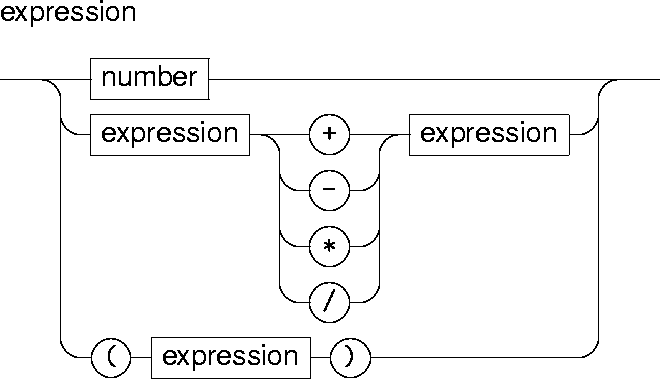
Expressions
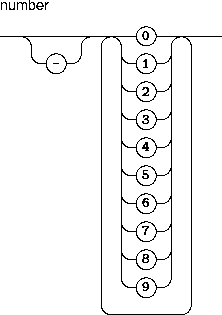
An expression is formed from numbers and the four standard arithmetic operations:Arithmetic operations have their usual precedence: multiplication and division have higher precedence than addition and subtraction. All arithmetic operations are left-associative. Parenthesis are used to impose an precedence or associativity different from the default ones.A number is a decimal integer, possibly preceded by a minus sign:
The number-0is identical to the number0.White-space characters may appear anywhere within an expression, but may not appear within a number; in particular, no white-space characters should follow the minus sign in negative numbers.
Expression evaluation
Expressions are evaluated with 31 bits of precision; that is, the absolute value of any value computed is assumed to be representable with at most 31 bits. An overflow occurs when the absolute value of an expression can't be represented in at most 31 bits.