Operating Systems Lecture Notes
2014 October 7 • Managing Concurrency
Outline
- The problem.
- Unrestrained concurrent access.
- The general solution.
- Properly constrained concurrent access.
- Strictly sequential access otherwise.
- Solution details.
Problem Background
- Given the globals (a circular queue)
widget q[N] q-size = 0 head = tail = 0
and the two functions
runp() loop w = f() while q-size ≡ N {} q[tail++] = w ++q-sizec() loop while q-size ≡ 0 {} w = q[head++] --q-size g(w)p()andc()in separate threads.
Problem Illustrated
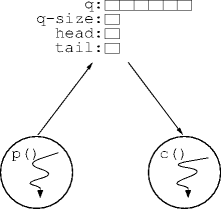
The Problem
-
p()andc()have interfering access toq-size.p():++q-size
c():--q-size - The problem is uncoordinated read and write access to shared state.
|
| get ri, @q-size get ri, @q-size sub ri, 1 put ri, @q-size add ri, 1 put ri, @q-size get ri, @q-size sub ri, 1 get ri, @q-size add ri, 1 put ri, @q-size put ri, @q-size |
| \(\vdots\) |
A Solution
- Coordinate access via turn-taking.
widget q[N] q-size = 0 head = tail = 0 turn = 'p'
p() loop w = f() while turn ≠ 'p' {} q[tail] = w tail = tail+1 % N ++q-size turn = 'c'c() loop while turn ≠ 'c' {} w = q[head] head = head+1 % N --q-size turn = 'p' g(w)
Problem Solved?
- Turn taking solves the problem, but
- Too much concurrency lost.
- The while loop is wasteful.
- Doesn't handle many producers and consumers.
- Violates several technical properties discussed later.
- Is there a better way?
Ruinous Competition
- The problem is uncoordinated concurrent access to shared data.
- All three properties — uncoordinated, concurrent, shared — are required.
- Eliminating any one of the properties solves the problem.
- Coordination with concurrency is hard, needs big machinery.
- Sharing is a property of the programming language.
Mutual Exclusion
- Suppose we could switch-off concurrency in a region of code.
- At most one thread in the region, ever.
- No concurrency, no competition, no problems.
- Mutual exclusion: insuring at most one thread in a code region.
- Protect shared access in regions of mutual exclusion.
Mutual Exclusion Example
- Mutual exclusion region.
widget q[N] q-size = 0 head = tail = 0
|
|
Critical Sections
- A critical section is a region of mutual exclusion.
- Sometimes the region requiring mutual exclusion.
-
\(\vdots\) enter cs cs exit cs \(\vdots\) - A critical section is delimited by an entry and exit point.
- Threads wait at the entry point until the critical section is empty.
- Then a waiting thread enters.
Critical Section Rules
- A critical section cs should follow three rules:
- Mutual exclusion: there’s at most one thread in cs.
- Waiting progress: if cs is empty and threads are waiting on cs, one of those threads eventually enters cs.
- Bounded waiting: every thread waiting on cs eventually enters cs.
- These rules are given in various ways, but: mutual exclusion, progress, and no starvation.
The Independence Rule
- Sometimes there’s a fourth critical-section rule:
- Independence: Only threads waiting on cs influence which thread enters cs.
- This rule eliminates the turn-taking solution to the two-thread
producer-consumer problem.
- But sometimes a little outside influence is useful.
- Client-server scheduling, for example.
Multiple Critical Sections
|
|
Local vs Global Mutual Exclusion
- Global mutual exclusion: At most one thread in all critical
sections.
- Also known as one big lock.
- Local mutual exclusion: At most one thread in any critical section.
- Global mutual exclusion: easy to implement and use, hard to get wrong, prevents concurrency benefits.
- Local mutual exclusion: hard to implement, easy to use and get wrong, preserves concurrency benefits.
Implementing Critical Sections
- How do critical sections provide mutual exclusion, progress, and
no starvation?
- That is, how are critical sections implemented?
- The key is implementing the “enter cs” and “exit cs” statements.
- There is a hierarchy of solutions.
|
|
The Return of Turn-Taking
- Simple turn-taking doesn’t obey Independence.
- And is fundamentally broken for more than two threads.
- Independence: only waiting threads have a say.
- What about ignoring threads not waiting?
- Which makes sense: if a thread’s not waiting, who cares?
Peterson’s Algorithm.
- Peterson’s algorithm is new (sorta), improved turn-taking.
- Given critical section cs threads t0 and t1, the
globals for cs are
int turn = 1 boolean involved[2] = { false, false } -
involved[i]iff tiis waiting to enter or in cs. -
turn = imeans “in case of a tie, tienters the cs.”
Peterson’s Algorithm..
- To enter cs, t
idoes (jrepresents the other thread,j = (i + 1) mod 2).involved[i] = true; turn = j while involved[j] && turn ≡ j { } - When leaving the cs, t
idoesinvolved[i] = false;
Observations
- A completely user-space solution.
- Local mutual exclusion.
- An example of a spin lock.
- A thread burns CPU cycles in
while involved[j] && turn ≡ j { }until it falls out.
- A thread burns CPU cycles in
- A Peterson tournament tree handles n threads per critical section.
Disabling Interrupts
- Without interrupts, a thread can’t be pre-empted from the CPU.
- And a thread locked in the CPU has exclusive access to everything.
- Including critical sections.
- Disable interrupts for mutual exclusion.
- enter cs ≡ disable interrupts.
- exit cs ≡ enable interrupts.
- The thread in the critical section owns the CPU.
Observations
- Interrupt play is cheap, natural and effective.
- One privileged instruction, plus the context switch.
- Global mutual exclusion with no concurrency. At all. Anywhere.
- And progress, but also starvation.
- Without interrupts, working computer systems are impossible.
- Multi-engine fail, usually.
Stones and Bowls
- Some rules for critical section cs:
- There's a bowl at enter cs.
- A thread in cs must hold the stone.
- The thread at exit cs puts the stone in the bowl.
- A thread at enter cs wanting into cs must take the stone from the bowl first.
- These rules provide mutual exclusion, progress, and starvation. And independence.
Modern Stones and Bowls
- The modern version of the stone in a bowl is the
test-and-setinstruction.- The bowl is a boolean variable b.
- If b = true, the bowl holds the stone.
- If b = false, the bowl is empty.
-
test-and-setis a non-interruptable, non-privileged instruction in modern architectures.- SPARC v9
ldstubinstruction.
- SPARC v9
test-and-set
- The effect of
test-and-setisbool test-and-set(bool * bowl)
bool b = *bowl *bowl = false return b - Set a variable to false and return the variable's previous value.
- If the stone's in the bowl,
test-and-setreturns true and the bowl is empty.- Otherwise
test-and-setreturns false.
- Otherwise
Test-and-Set Critical Sections
- A
test-and-setcritical section:bool bowl-csi = true enter csi while !test-and-set(bowl-csi) { } exit csi bowl-csi = true -
bowlis usually calledlock.
Summary
- The problem is unrestrained, shared, concurrent access.
- The general solution is constraints, or no sharing, or no concurrency.
- Control concurrency with mutual exclusion.
- Critical sections delimit regions of mutual exclusion.
| This page last modified on 2014 October 9. |
