Intelligent Systems Lecture Notes
19 October 2011 • Uncertainty
Outline
- Planning review.
- Uncertainty
- Uncertain knowledge.
- Incomplete world knowledge.
- Possible worlds.
- Probabilities
Planning
- The planning world is an n-tuple of features.
- Each feature contains a value from a set of possible values.
- An agent is part of the world (has features in the world).
- The agent acts on the world, changing feature values.
- A goal is a world with particular feature values.
- The agent plans actions that cause the world to match the goal.
Assumptions
- Assumptions allow and simplify planning.
- They also make planning less realistic.
- Weaker assumptions provide greater realism, at greater cost (usually).
- Two particularly strong assumptions are
- agent actions are deterministic (perfectly predictable), and
- the agent has complete world knowledge.
- Let's weaken them.
Example

Uncertain Knowledge
- Agent actions may not have predictable results.
- Agents have incomplete world knowledge.
- An agent needs to
- reason about and with uncertain knowledge, and
- make decisions based on uncertain knowledge.
- Living in an uncertain world is gambling.
Kinds of Uncertainty
- There are different kinds of uncertainty.
- Each with its own calculus.
- But sharing a common substrate (more or less).
- Relaxed assumptions cause two kinds of uncertainty:
- Outcome uncertainty (semi-deterministic).
- World knowledge uncertainty (world beliefs).
- There's other low-hanging fruit on this tree.
Outcome Uncertainty
- An agent has outcome uncertainty when
- it knows all possible action outcomes,
- but not a particular one with certainty.
- Classic example: rolling a die.
- Outcome uncertainty is (can be) handled with basic probability and
statistics.
- Probability also forms the substrate for handling other uncertainties.
Incomplete World Knowledge
- An agent with incomplete world knowledge no longer knows the
world perfectly.
- Due to, for example, missing or incorrectly perceived sensory information.
- Incomplete world knowledge transforms agent world knowledge into
world beliefs.
- Knowledge to beliefs represents the loss of certainty.
- World beliefs are (can be) handled with subjective probability (Bayesian statistics).
Random Variables
- In probability, world features are called random variables.
- A simple random variable X represents a value from the domain dom(X).
- A composite random variable is a tuple of simple random
variables
\(\langle\) X1, …, Xn\(\rangle\)
- representing a value from the domain
dom(X1) \(\times \cdots \times\) dom(Xn)
Possible Worlds
- A possible world equates a value to each identified random
variable.
- \( \omega \models \) X = v means random variable X has value v in world \(\omega\).
- “\(\omega \models\) X = v” : \(\omega\) satisfies or models X = v.
- Note the possibility of don't cares.
- \(\Omega\) is the set of all possible worlds.
- For the most part, assume \(\Omega\) is finite.
World Propositions
- The random-variable equality X = x is a world proposition.
- If \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) are world propositions, then so are
\(\alpha \wedge \beta\), \(\alpha \vee \beta\), and \(\neg\alpha\).
\(\omega \models \alpha \wedge \beta\) means \(\omega \models \alpha\) and \(\omega \models \beta\).
\(\omega \models \alpha \vee \beta\) means \(\omega \models \alpha\) or \(\omega \models \beta\).
\(\omega \models \neg\alpha\) means \(\omega \not\models \alpha\). - \(\Omega(\alpha)\) is the set of possible worlds satisfying \(\alpha\).
- \(\Omega(\alpha) = \{ \omega \in \Omega\;|\;\omega \models \alpha \}\).
Probabilities
- If \(\Omega\) is finite, define the probability measure
Pr : \(\Omega \rightarrow \) [0..1]
such that the two properties
hold.Pr(\(\Omega\)) = 1.
If \(\Omega(\alpha_1), \ldots, \Omega(\alpha_n)\) are pairwise disjoint, then
Pr(\(\Omega(\alpha_1)\;\cup\;\ldots\;\cup\;\Omega(\alpha_n)\)) = Pr(\(\Omega(\alpha_1)\)) + \(\cdots\) + Pr(\(\Omega(\alpha_n)\)).
Probability Semantics
- What does Pr(\(\alpha\)) mean?
- There are lots of semantics; one simple one is the frequency
interpretation:
Pr(\(\alpha) = \frac{|\alpha|}{|\Omega|}\)
The probability Pr(\(\alpha\)) is the fraction of all possible worlds taken up by \(\alpha\).
- Remember that \(\Omega\) is assumed finite.
- Infinite \(\Omega\) can be handled by other means.
Just Checking
- Property 1:
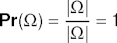
- Property 2:
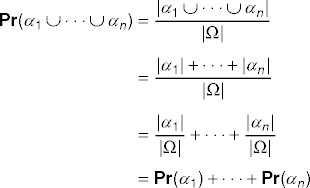
- assuming \(\alpha\)i \(\cap\;\alpha\)j = { } for 1 \(\leq\) i \(<\) j \(\leq\) n.
|
|
|
Example
- Remember this:
ALOC { office, lab, coffee, mail } AHC boolean AHM boolean SWC boolean MW boolean - \(|\Omega| =\) 64, a = \(\Omega(\)ALOC = office), |a| =
16.
- Pr(a) = |a|/\(|\Omega|\) = 16/64 = 1/4.
Picturing Frequencies
- Venn diagrams are helpful when understanding frequency interpretations
of probability.
- But they don't scale with complexity.
- \(\Omega\) is the universe.
- \(\Omega(\alpha)\) is a circle within the universe.
Properties Pictured
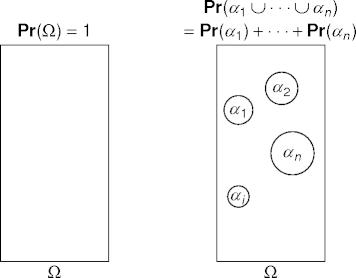
Summary
- More realistic planning worlds requires accepting uncertainty.
- Uncertainty comes in many forms, each handled differently.
- But sharing a common base.
- Agent actions may be non-deterministic.
- Classic probability can deal with non-determinism.
References
- Confidence Factors, Probability, Belief Networks, and Multivalued Logic (Chapter 10) in Intelligent Systems by Robert Schalkoff, Jones and Bartlett, 2011.
- Quantifying Uncertainty (Chapter 13) in Artifical Intelligence, third edition, by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, Prentice Hall, 2010.
- Vagueness, Uncertainty, and Degrees of Belief (Chapter 12) in Knowledge Representation and Reasoning by Ronald Brachman and Hector Levesque, Morgan Kaufmann, 2004.
Credits
- Are your small kitchen appliances properly firewalled? by Callie Carroll under a Creative Commons BY NC SA license.
| This page last modified on 2011 October 18. |
