Intelligent Systems Lecture Notes
25 November 2011 • Reinforcement Learning
Outline
- Markov decision processes.
- Reinforcement learning.
- Passive reinforcement learning.
- Direct utility estimation.
- Active dynamic programming.
- Temporal-difference learning.
- Passive reinforcement learning.
Markov Decision Processes
- S = { 11 12 13 21 23 31 32 33 41 42 43 }.
- A = { l r u d }.
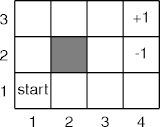
S' 11 12 21 13 ··· A u u u u ··· S 11 11 11 11 ··· Pr(S' | S, A) 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 ··· S' 43 33 23 32 ··· A r r r r ··· S 33 33 33 33 ··· R(S, A, S') 1 -0.04 -0.04 -0.04 ···
Reinforcement Learning
- An agent works in a fully observable world.
- The agent uses a Markov decision process, but the agent doesn’t know
- the transition function Pr(), and
- the reward function R().
- The reinforcement learning problem determines an optimal policy, or close to it.
A Warm-Up Problem
- The agent has π. How can it find Vπ?
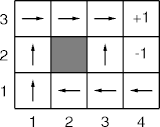
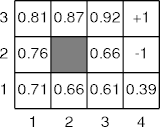
π Vπ - The passive learning problem determines how good π is (or, it finds Vπ using π).
Passive Learning
- The general idea is to run experiments, record the results, and analyze the history.
- A trial is a sequence of state, action, reward triples
- s0, a0, r0, s1, a1, r1, …
- s0 is the initial state; the last state sk is a terminal state.
- Assume the discount rate is γ = 1.
Estimating Vπ()
- Given a trial of k steps
s0, a0, r0, …, si, ai, ri, …, sk, –, rk
- estimate the utility of si as the sum of the rewards from steps i through k.
- Vπ(si) is the mean of all sums for si for all trials.
- This is known as direct utility estimation.
Example
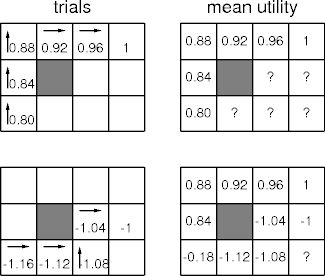
Observations
- Direct utility estimation doesn’t know about the stochastic relation
among squares.
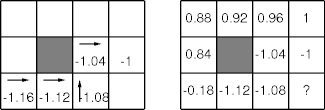
- The mean utility for 31 should leach off 10% of the mean utility for 33.
- Direct utility estimation can converge slowly.
Improving DUE
- To improve on direct utility estimation, estimate the transition function Pr() too.
- Once Pr() is known, everything in in the right-hand side of
Qπ(s, a) = \(\sum\)n Pr(n | s, a)(R(s, a, n) + γVπ(n))
- has been estimated, providing an estimate for Qπ().
- And Qπ() leads to Vπ().
Estimating Pr()
- Counts taken from trials estimate the transition conditional probabilities.
- Given
…, 11, up, 12, …
…, 11, up, 21, …
…, 11, up, 12, …
- then
Pr(12 | 11, up, 11) = 2/3
Pr(21 | 11, up, 11) = 1/3
Finding Vπ()
- Once Qπ() is in hand, Vπ() can be found by solving the related linear-equation set.
- Alternatively, the estimates can be created iteratively using
adaptive dynamic programming (ADP).
- Adaptive dynamic programming provides continuous results (of varying quality), and fast convergence.
- Adaptive dynamic programming is a variant of MDP policy iteration.
ADP Algorithm
| passive ADP(sn, rn) | |||||
| if V[sn] = null then V[sn] = R[sn] = rn | |||||
| if sc ≠ null | |||||
| Nsa[sc, ac]++ | |||||
| Nssa[sn, sc, ac]++ | |||||
| for each s ∈ S do | |||||
| Pr[s, sc, ac] ← Nssa[s, sc, ac]/Nsa[sc, ac] | |||||
| V ← the solution to the related linear equations | |||||
| if sn is terminal | |||||
| then sc, ac ← null | |||||
| else sc, ac ← sn, π[sn] | |||||
| return ac | |||||
Further Improvements
- After picking up Vπ() and Pr() from the traces, is there anything
left top pick up?
- And if so, how can we exploit it to get better results?
- DUE and ADP compute means.
- More importantly, mean computations over related, and improving, data.
- What can you do with means?
- But first, what’s wrong with them?
Mean Problems
- The straightforward mean calculation
(v1 + \(\cdots\) + vn)/n
treats (weights) all values the same. - As an algorithm converges, later values are better (more accurate) than earlier values.
- A better mean would weight later values over earlier values.
Computing Averages
-
Let Ak be the average of k samples Ak = (v1 + \(\cdots\) + vk)/k Multiply by k kAk = v1 + \(\cdots\) + vk - 1 + vk = (k - 1)Ak - 1 + vk Divide by k Ak = (1 - 1/k)Ak - 1 + vk/k Let αk = 1/k Ak = (1 - αk)Ak - 1 + αkvk = Ak - 1 + αk(vk - Ak - 1)
The Temporal-Difference Error
- Rewriting (v1 + \(\cdots\) + vk)/k as
Ak - 1 + αk(vk - Ak - 1)
- emphasizes two values:
- vk - Ak - 1, the temporal-difference error,
- αk, the learning rate.
- The learning rate is a knob controlling the value of the present (away from 0) over the past (near 0).
Learning Rate
- The learning rate αk = 1/k is a function
of k.
- New values add decreasingly smaller amounts to the average.
- Converges to the mean, doesn’t exploit more accurate or representative values.
- A constant learning rate α ∈ (0, 1]
- Favors new values over the average.
- Responds to change, but doesn’t converge to the mean.
Learning-Rate Example
Move the mouse pointer over the lighter curves at the data points (bends in the curve) to highlight the curve.
The Q-Learning Algorithm
| Q-learning(S, A, γ, α) | |||||
| Q[s, a] ← whatever | |||||
| s ← start state | |||||
| repeat | |||||
| pick a from A and perform it in state s | |||||
| observe the reward r and next state n | |||||
| Q[s, a] ← Q[s, a] + α(r + γmaxan Q[n, an] - Q[s, a]) | |||||
| s ← n | |||||
| until done | |||||
Summary
- Reinforcement learning recovers information from a partial Markov decision process.
- Passive reinforcement learning judges policy from execution histories.
- When life gives you lemons, take the mean.
- Possibly using temporal differences.
References
- Reinforcement Learning (Chapter 21) in Artifical Intelligence, third edition, by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, Prentice Hall, 2010.