Outline
- Interface examples.
- Interface design.
Interface Example
interface uBloggingFeed {
void register(String user, String password);
String [] read();
void update(String msg);
}
class TwitterFeed
implements uBloggingFeed {
void register(String user, String password) { ... }
String [] read() { ... }
void update(String msg) { ... }
}
Java interfaces
- The
uBloggingFeed interface.
- The
TwitterFeed class implements the uBloggingFeed interface by
implementing the instance methods defined in the interface.
-
TwitterFeed can implement other methods too.
Comments
- An interface isn’t a class.
- Interfaces can’t be instantiated (no
new calls).
- An interface doesn’t have an execution behavior (no method bodies)
- A class uses the
implements modifier to indicate which interfaces
it provides.
- A class can implement several interfaces.
class X
implements uBloggingFeed, IPod, { ... }
Why Interfaces?
- Interfaces support good software development.
- Well defined boundaries between software components.
- Interfaces define types.
- Added subtype polymorphism.
- Reduces code duplication.
Interface Type Examples
Map<String, Command> h1
= new HashMap<String, Command>();
Map<String, Command> h2
= new TreeMap<String, Command>();
List<Object> t1 = new ArrayList<Object>();
List<Object> t2 = new LinkedList<Object>();
Code Duplication Example.
- Two implementations:
-
TwitterFeed connects to Twitter.
-
IdenticaFeed connects to Identi.ca.
- A client uses both
TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed.
- The client defines a
poll() method for new messages.
- What does
poll() look like?
Code Duplication Example..
-
TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed are different types.
public static void poll(TwitterFeed) f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
public static void poll(IdenticaFeed f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
Comments
-
TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed are different types, and
can’t share poll().
- Even though the code within each method is identical.
- How can
TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed share poll()?
Interfaces vs Sharing.
interface uBloggingFeed {
String [] poll();
// and so on
}
Class TwitterFeed
implements uBloggingFeed {
public String [] poll() { ... }
// and so on
}
Class IdenticaFeed
implements uBloggingFeed {
public int poll() { ... }
// and so on
}
Interfaces vs Sharing..
class Client {
public static void poll(uBloggingFeed f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
// and so on.
}
- Now
poll() can accept both TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed
instances.
Subtype Polymorphism
- Both
TwitterFeed and IdenticaFeed “behave like” an
uBloggingFeed.
- Interfaces define types.
- Implementing classes define subtypes of the interface type.

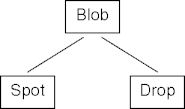
Ahierarchical Types
- Unlike ancestors and descendant classes, interface types don’t form a
tree.
- A class may implement many interfaces.
- An interface may be implemented by many classes.
Code Sharing
- A class can
- Implement many interfaces, but
- extend only one class.
- To share code between two classes
- Put the shared code in a common superclass.
- But interfaces can’t contain code.
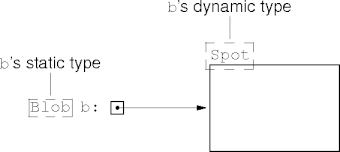
Static vs Dynamic Types
- Every variable has a static or compile-type or declared type.
- Determined by the variable declaration.
- Known at compile time.
- A variable’s static type doesn’t change.
- Every class instance has a dynamic or runtime type.
- Determined when the instance is created via
new.
- Can’t be determined at compile time.
- an instance’s dynamic type doesn’t change.
Example
int i = 3, j = 4;
Integer x = new Integer(i + 3*j - 1);
System.out.println(x.toString());
Variables i, j and the expression i + 3*j - 1 have
int static type.
- Variable
x and the expression new Integer(...) have static
type Integer.
- The expression
x.toString() has static type String.
- The instance created by
new Integer(...) has dynamic type
Integer.
References vs Primitive Types
- A reference type.
- Classes, interfaces, arrays.
-
Integer for example.
- Primitive types.
-
int, boolean, char, and so on.
Why Both int and Integer?
- Some data structures work only with reference types.
-
Hashtable, Vector, Stack and so on.
- Primitive types are more efficient.
-
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ... }
Upcasting and Downcasting
- Applies to reference types only.
- Used to assign the value of an expression of one (static) type to a
variable of another (static) type.
- Upcasting: subtype → supertype
- Downcasting: supertype → subtype
- The subtype invariant:
Given an expression E producing an object O, O’s dynamic
type is a subtype of E’s static type.
Upcasting
- Example upcast:
-
Object x = new Integer(13);
- The rhs’s static type must be a subtype of the lhs’s static type.
- Upcasting is always type correct.
- The subtype invariant is automatically preserved.
Downcasting
- Example downcast:
- In any downcast, the an object’s dynamic type must be a subtype of the
cast expression’s static type.
- The subtype invariant may or may not hold.
- A
ClassCastException results if it doesn’t.
- Requires a run-time check.
Runtime Checking
- Runtime type checking required because an object’s dynamic type may not
be known at compile time.
void red() {
white(new String("x"));
}
void white(Object y) {
int z = ((Integer) y).intValue();
Interface Upcasts
- Upcasting with interfaces is common.
uBloggingFeed p1 = new IdenticaFeed();
uBloggingFeed p2 = new TwitterFeed();
-
p1 and p2 have uBloggingFeed static type.
- The
new expressions have types that are subtypes of uBloggingFeed.
- The subtype invariant is maintained.
Why Upcast?
- Subtyping and upcasting can be used to avoid code duplication.
- For example, you and the client agrees on the
uBloggingFeed interface.
interface uBloggingFeed {
void register(String user, String password);
String [] read();
void update(String msg);
}
Sharing With Interfaces
interface uBloggingFeed {
String [] read();
// and so on
}
Class TwitterFeed
implements uBloggingFeed {
public String [] read() { ... };
// and so on
}
Class IdenticaFeed
implements uBloggingFeed {
public String [] read() { ... };
// and so on
}
class Client {
public static void poll(uBloggingFeed f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
// and so on.
}
Method Dispatch.
class Client {
public static void poll(uBloggingFeed f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
// and so on.
}
- Which
read method is invoked?
- Depends on
p’s dynamic type (TwitterFeed or
IdenticaFeed).
- Which ever type it is, it provides a
read() method.
Method Dispatch..
class Client {
public static void poll(uBloggingFeed f) {
final String msgs [] = f.read();
if (msgs.length > 0) { ... }
}
// and so on.
}
- Check at compile time p’s static type (
uBloggingFeed)
for read()’s signature.
- Check at runtime p’s dynamic type for the
read()
method.
- The compile-time check guarantees it’ll be there.
Comments
- Up- and downcasting allow the class instance to be viewed at compile
time as a different static type.
- Casting is a bookkeeping operation; nothing actually changes.
- The class instance’s dynamic type remains the same.
- The expression’s static type doesn’t change.
Polymorphic Data Structures
uBloggingFeed [] feeds = new uBloggingFeed[9];
feeds[0] = new TwitterFeed();
feeds[1] = new IdenticaFeed();
feeds[i] has uBloggingFeed static type.
- The
new expressions have uBloggingFeed subtypes as static types.
Type Compatibility
- Two reference types are type compatible if one is an ancestor
of the other.
- An ancestor instance can be assigned to a descendant variable.
- This is known as upcasting.
- The compiler upcasts implicitly.
- A descendant instance requires an explicit downcast to be
assigned to an ancestor variable.
Compatability Example
Static and Dynamic Types
- Every reference variable has two types: a static and dynamic type.
- Assuming the reference variable is non-null.
- A reference variable’s static type is its declared type (that
is, class).
- A reference variable’s dynamic type is the type (that is,
class) of the referenced instance.
- If the reference variable’s null, there’s no dynamic type.
Type Example
Checking Dynamic Types
- The
instanceof binary operator tests dynamic types.
if (p instanceof TwitterFeed) { ... }
-
i instanceof C is true if i’s dynamic type is a
subtype of C.
- Often used to make sure downcasts will succeed.
- Frequently interpreted as a code smell.
instanceof Example
- Suppose
JaikuFeed but not IdenticaFeed implements the
search() method.
void search(uBloggingFeed[] feeds) {
for (uBloggingFeed f : feeds)
if (f instanceof JaikuFeed) {
JaikuFeed f = (JaikuFeed) feeds[i];
f.search();
}
}
Avoid Useless Downcasting
- Legal but bad:
void moveAll(uBloggingFeed[] feeds) {
for (uBloggingFeed p : feeds)
if (p instanceof TwitterFeed)
((TwitterFeed) feeds[i]).move("N");
else
((IdenticaFeed) feeds[i]).move("N");
}
- Legal and good:
void moveAll(uBloggingFeed[] feeds) {
for (uBloggingFeed p : feeds)
feeds[i].move("N");
}
Subinterfaces
- Suppose you want to extend the interface to include more methods.
-
uBloggingFeed defines register(), read(), and update()
methods.
-
JaikuFeed also defines the search() method.
- There are two approaches:
- Create a brand new
JaikuFeed interface.
- Extend the
uBloggingFeed interface to create JaikuFeed.
Subinterface Example
interface uBloggingFeed {
void register(String user, String password);
String [] read();
void update(String msg);
}
interface JaikuFeed
extends uBloggingFeed {
String [] search(String keywords);
}
-
uBloggingFeed is a superinterface of JaikuFeed.
-
JaikuFeed is a subinterface of uBloggingFeed.
-
JaikuFeed is a subtype of uBloggingFeed.
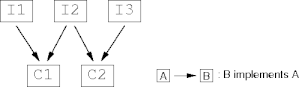
Subinterface Properties
- An interface can extend multiple superinterfaces.
- A class that implements an interface must implement all methods
declared in all superinterfaces.
- The implementing class can be considered a subtype of all implemented
interfaces.
Summary
- Interfaces can be used to structure software and for subtyping.
- Subtyping is a powerful technique for designing and implementing
software.
- It results in subtype polymorphism.
|
This page last modified on 22 September 2010.
|

|