Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture Notes
10 September 2009 • Types and Polymorphism
Outline
- Types and polymorphism.
- Java types.
- Java typing.
- Primitive and reference types.
- Class-type relations.
Types
- A Java program defines a universe of values.
- Each value is tagged with a name called its type.
- The value
trueis tagged with thebooleantype.
- The value
- A value’s type determines the sensible operations on that type.
-
sqrt(true)???
-
Strong Typing
- A program’s variables hold values from the program’s value universe.
- Each variable is tagged with a type name.
int i; double sqrt(double x) { ... } - Java is strongly typed: a variable of type t can only hold
values of type t.
i = true;sqrt(true)
Type Strictness
- Sometimes types don’t matter much.
- A stack can hold all value types.
- Strong typing gets in the way in those cases.
- A stack for
ints, a stack forbooleans, and so on.
- A stack for
- It is useful to selectively ignore types when they don’t matter.
Polymorphism
- Polymorphism is a family of techniques for selectively ignoring types when convenient.
- Exploiting polymorphism in data structures makes them more general and
more useful.
- The data structures can ignore types where possible.
- The broader the range of values accepted, the more useful the data structure.
Java Types
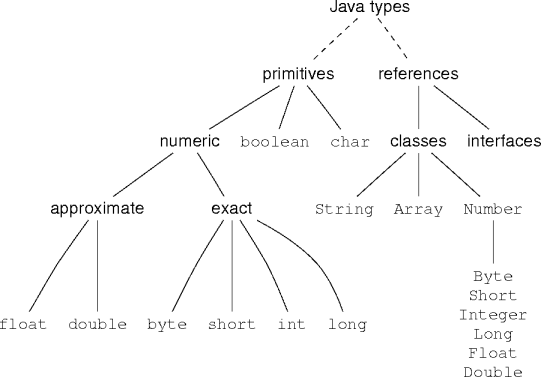
Reference Types
- A Java reference type is analogous to a C++ pointer to class
instance.
- Except: no touching.
- All accesses to Java class instances are through reference values.
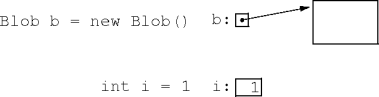
Primitives vs. References
- Primitive types are incompatible with reference types.
-
Will this method compile?
void m() {Objecto = 42; }
Primitives as References
- A primitive has to be converted to a class instance to be treated as a
reference.
void m() { Object o = newInteger(42); }
References as Primitives
- Similarly a reference has to be converted to a primitive.
- Using
primitive-typeValue()injava.lang.Number. - This is known as unwrapping the primitive.
-
hashTablemapsStrings toints.
-
void m(String key) if (hashTable.containsKey(key)) int i = ((Integer) hashTable(key)).intValue() - Using
Automatic Conversions
- Wrapping and unwrapping primitives manually is a pain.
- And necessary prior to Java 5.
- Java 5 automatically converts between primitive-type values and
Numbers.
- The conversions are called autoboxing (wrapping) and
auto-unboxing (unwrapping).
- Usually omit the “auto”.
- The conversions are called autoboxing (wrapping) and
auto-unboxing (unwrapping).
Boxing Examples
void m() {
Object o = 42;
}
void m(String key) {
if (hashTable.containsKey(key))
int i = hashTable(key);
}
Java Types
Class Types
- Class instances are Java values, tagged with the class name.
- The class methods determine the allowable operations on instances.
- What’s the relation between class types?
The IS-A Relation
class Dictionary
void add(Key k, Value v) { ... }
Value find(Key k) { ... }
void delete(Key k) { ... }
class LinkedListDictionary
void add(Key k, Value v) { ... }
Value find(Key k) { ... }
void delete(Key k) { ... }
class HashTableListDictionary
void add(Key k, Value v) { ... }
Value find(Key k) { ... }
void delete(Key k) { ... }
IS-A Abstraction
- If class A looks like class B’s, then A IS-A B.
- Claim: An A is just a good as a B to B’s clients.
- Justification: any client of B can also be a client of A.
Inheritance
- Inheritance is a realization of the IS-A relation in
object-oriented programming languages.
A inherits from B A IS-A B - Inheritance specifies a behavioral relation between classes.
The Inheritance Relation
- “A IS-A B” corresponds to “A inherits-from
B”.
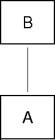
- A is the child, subclass, derived class, descendant (relative to B).
- B is the parent, superclass, base class, ancestor (relative to A).
- The
extendsclass modifier signals inheritance:class Child extends Parent { ... }- A child has one parent (single inheritance).
Why Inheritance?
- All the parent’s non-private instance variables and methods are
available to (are inherited by) the child instance.
class Dictionary { void add(Key k, Value v) { ... } Value find(Key k) { ... } void delete(Key k) { ... } } class LinkedListDictionary extends Dictionary { }
Class Compatibility
- Two classes are type compatible if one class is an ancestor of the other.
- An ancestor instance can be assigned to a descendant variable.
- This is known as upcasting.
- The compiler upcasts implicitly.
- A descendant instance requires an explicit downcast to be assigned to an ancestor variable.
Compatibility Example
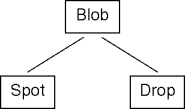
class Blob { ... }
class Spot extends Blob { ... }
class Drop extends Blob { ... }
|
|
|
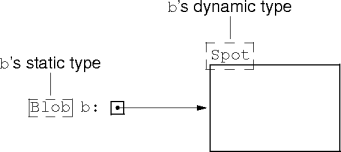
Static and Dynamic Types
- Every reference variable has two types: a static and dynamic type.
- Assuming the reference variable is non-null.
- A reference variable’s static type is its declared type (that is, class).
- A reference variable’s dynamic type is the type (that is,
class) of the referenced instance.
- If the reference variable’s null, there’s no dynamic type.
Type Example
- The dynamic type’s a descendant of the static type.
- The dynamic type may equal the static type.
class Blob { ... }
class Spot extends Blob { ... }
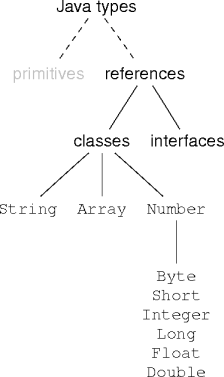
The Object Class
- The Object class is the only class without a parent.
- Every class has Object as an ancestor.
- Either explicitly or implicitly.
class Blob extends Object { ... } class Spot { ... } class Drop extends Spot { ... }
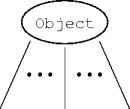
- Either explicitly or implicitly.
Object Polymorphism
- Because every class is-an Object, Object provides a simple form of
polymorphism.
class Stack void push(Object o) { ... } Object pop() { ... }- This is a stack that can hold any class instance.
- And primitives via autoboxing.
- This is a stack that can hold any class instance.
- What is the implicit protocol in this polymorphism?
Casting
- Object polymorphism requires up- and downcasting.
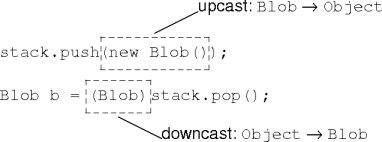
- Incessant downcasting makes Object polymorphism tedious and dangerous.
- The compiler handles the upcasting.
Object-Casting Problems
- Indiscriminate object casting is confusing and dangerous.
stack.push("blah"); use(stack); stack.push(new Blob()); use(stack); stack.push(stack); use(stack); - What does
use()look like?void use(Stack s) ??? e = (???) s.pop(); // and so on.
Generics
- Java 5 replaces Object polymorphism with generics.
- Actually, it automates the downcasting in Object polymorphism.
- Confusion and failures in generics are a consequence of this.
- Java versions prior to 5 had only Object polymorphism.
- Object polymorphism also exists in various corners of post-1.4 Java.
Summary
- Types are important, except when they aren’t.
- Polymorphism is there for you when they aren’t.
- Java distinguishes primitive and reference types.
- Not so much since Java 5, but still...
- The Object class provides a week form of polymorphism.