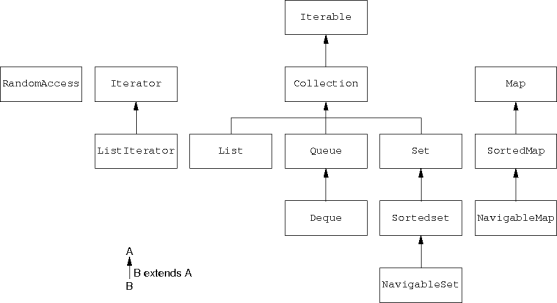

'
Collection interface extends the
Iterable interface.
add(), addAll()
clear(), remove(), removeAll(),
retainAll()
contains(), isEmpty(), size()
toArray()
UnsupportedOperationException when inapplicable optional methods are called.
addAll() signature is
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
The removeAll() signature is
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
Why are the type variable declarations in the two signatures different?

'
Queue interface extends the Collection interface.
| Throws | Returns | |||
| exception | special value | |||
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) | ||
| Remove | remove() | poll() | ||
| Examine | element() | peek() |
Deque interface extends the Queue interface.
Queue operations.
addFirst(e), removeFirst(), getFirst() offerFirst(e), pollFirst(), peekFirst() addLast(e), removeLast(), getLast() offerLast(e), pollLast(), peekLast()

'
List interface is as expected.
void add(int index, E element) E get(int index) boolean remove(int index) ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
ListIterator interfaces extends the
Iterator interface.
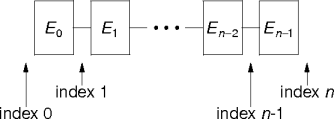
void add(E e)* boolean hasNext() boolean hasPrevious() E next() int nextIndex() E previous() int previousIndex() void remove()* void set(E e)* *optional
next() and previous() methods
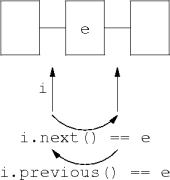
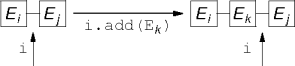
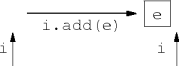
remove() removes the element returned by next() or previous().
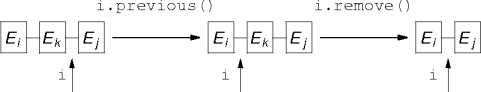
next() or previous() must be called before each call to remove().
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean xAll(Collection<?> c)
boolean b = true
for (Object o: c)
b = x(o) && b
return b
Set<Integer> iSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
HashSet<Integer> iSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
'
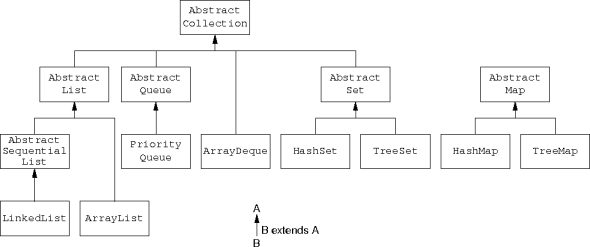
AbstractQueue class implements the
Queue interface.
public abstract class AbstractQueue<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Queue<E>
PriorityQueue extends AbstractQueue.
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implementsSerializable
LinkedList class extends the AbstractSequentialList class.
AbstractSequentialList class assumes a dynamic
link implementation.
ArrayList class implements a linked list assuming
indexing is cheap.
ArrayLists are more efficient than are Vectors.
ArrayLists aren’t thread safe and Vectors are.
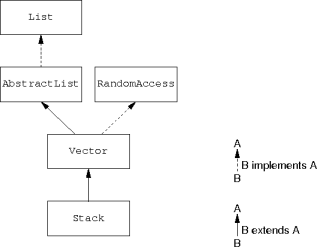
RandomAccess interface indicates efficient
indexing.
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) f(lst.get(i))
for (Iterator i = lst.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) f(i.next())
RandomAccess contains no methods; it just flags classes with
efficient indexing.
PriorityQueue class stores elements in increasing
priority order (a min-priority queue).
Comparable
interface.
Comparator
implementing, overriding the element comparable, if any.
Stacks were added to Java before the Collection
Framework (v. 1.0 vs v. 1.2).
'