
Algorithm design.
Data structures.
Algorithm analysis.

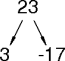
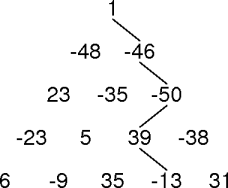
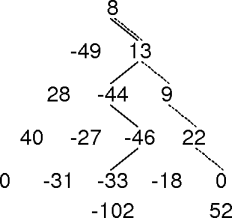
max-sum-path(triangle)
all-paths = all-paths(triangle)
max-path = pick(all-paths)
max-sum = path-sum(triangle, max-path)
for each path in all-paths
sum = path-sum(triangle, path)
if sum > max-sum
max-sum = sum
max-path = path
return [ max-sum, max-path ]
all-paths()).
path-sum()).
path-sum() is straightforward.
all-paths()?
|
|
|
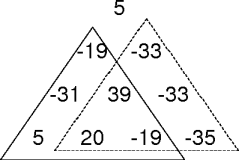
all-paths(row, col)
if row == N
return [ (row, col) ]
left-paths =
all-paths(row + 1, col)
right-paths =
all-paths(row + 1, col + 1)
paths = []
for path in left-paths + right-paths
paths += (row, col) ++ path
return paths
| Triangle | Solution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| size | time μsec | |||
| 5 | 251 | |||
| 10 | 6,270 | |||
| 15 | 267,000 | |||
| 20 | 8,620,000 | |||
| 25 | 283,000,000 | |||

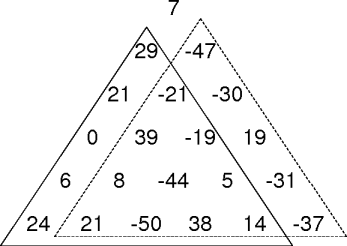
|
|
|
path[r,i].path is the max-sum path for the sub-triangle with
apex triangle[r,i].
path[r,i].sum is the max-sum value for the path.
max-sum-path(triangle)
for i = 1 to N
paths[N, i] = (triangle[N, i], [ (N, i) ])
for r = N - 1 to 1
for i = 1 to r
path = paths[r + 1, i]
if path.sum > paths[r + 1, i + 1].sum
path = paths[r + 1, i + 1]
paths[r, i] =
(path.sum + triangle[r, i],
(r, i) ++ path.path)
return paths[0, 0]
| Triangle | Solution Time μsec | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| size | All paths | Base up | ||||
| 5 | 251 | 434 | ||||
| 10 | 6,280 | 1,320 | ||||
| 15 | 267,000 | 2,330 | ||||
| 20 | 8,620,000 | 4,050 | ||||
| 25 | 283,000,000 | 9,080 | ||||
| 100 | 167,000 | |||||
| 500 | 6,750,000 | |||||
| 1000 | 36,400,000 | |||||