Computer Algorithms II Lecture Notes
28 October 2008 • Greedy Algorithms
Outline
- A scheduling problem.
- Exhaustive search.
- Greedy algorithms.
- Greedy algorithm design.
- Greed advantages and disadvantages.
- Greedy conditions
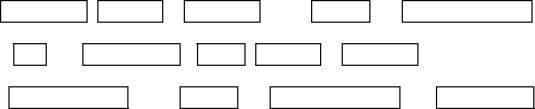
A Scheduling Problem
- Given an auditorium and a set of presentations, schedule the maximum
number of presentations possible.
- Each presentation has a start and end time.
- Each presentation requires exclusive use of the auditorium.
Exhaustive Search
- Look at every possible schedule.
schedule(presentations)
schedlue = { }
for i = 1 to 2size(presentations) - 1
s = get-schedue(i, presentations)
if valid(s) ∧ size(s) > size(schedule)
schedule = s
return schedule
Faster Scheduling
- Exhaustive search works if you don't schedule a lot of presentations often.
- But what if you do?
- Is there an alternative scheduling algoritm faster than exhaustive search?
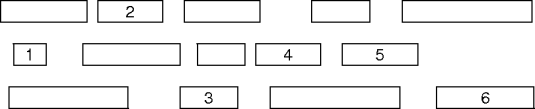
An Alterntive Scheduler
- Order the presentations by increasing finish time.
- Scan the ordered presentations by increasing finish time.
- Always schedule the next earliest finishing non-conflicting presentation.
Does It Work?
- Is the schedule S maximal?
- Suppose schedule S' has more presentations.
- Consider the first presentation in S and S'.
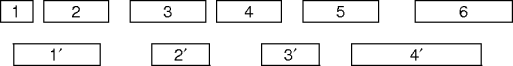
- 1 in S must end no later than 1' in S'.
- Replace 1' in S' with 1.
Does It Work??
- Schedules S and S' both agree on the first presentation.
- Remove it from both schedules.
- The remaining schedules must still be maximal.
- Otherwise the original schedules weren't maximal.
- Repeat the argument with the newly dimished schedules.
Does It Work???
- The two schedules always agree on the first presentation.
- The remaining schedules are always maximal.
- The two schedules must have the same number of elements.
- Or perhaps the second schedule wasn't maximal.
- Apparently the new scheduling algorithm works.
Greedy Algorithms
- A greedy algorithm always makes the next available best choice.
greed(p)
solution = { }
while choices-left(p)
solution ∪= best-choice(p)
return solution
- Problem: Schedule as many presentations as possible.
- Solution: Schedule the earliest finishing non-conflicting presentation.
Greedy Algorithm Design
- Got a problem? Solve it with greed!
- I wish I had some way of ordering the choices by importance.
- I wish I had some way of making the next choice.
- I wish I knew if greed worked in on this problem.
Example
- Assume a non-empty presentation list ordered by increasing finish times.
schedule(p[])
schedule = { 1 }
last = 1
for next = 2 to p.size()
if p[last].end ≤ p[next].start
schedule ∪= { next }
last = next
return schedule
Greed Advantages
- Always taking the best available choice is usually easy.
- It usually requires sorting the choices.
- Repeatedly taking the next available best choice is usually linear
work.
- But don't forget the cost of sorting the choices.
- Much cheaper than exhaustive search.
- Much cheaper than most other algorithms.
But...
- Create a schedule with maximum auditorium use.
- Greed repeatedly schedules the next largest non-conflicting presentation.
- Greed fails:
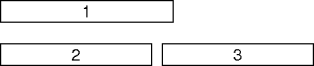
- Greed schedules 1, but { 2, 3 } is better.
Greed Disadvantages
- Greedy algorithms don't work for some problems.
- Despite their simplicty, correct greedy algorithms can be subtle.
- It's easy to fool yourself into believing an incorrect greedy algorithm is correct.
- “I can't think of a counter-example, so there are none.”
- Using greed is not an automatic.
Greedy Problems
- Why do greedy algorithms fail?

- Locally optimal choices may not be globally optimal.
Greedy Conditions
- There's no guarenteed way to recognize problems that can be solved by a greedy algorithm.
- But, a problem in which
- a locally optimal choice leads to a global optimum, and
- each remaining subproblem also leads to an optimal choice
can be solved with a greedy algorithm.
Summary
- Greedy algorithms can be a fast, simple replacement for exhaustive
search algorithms.
- Sometimes, which is the tricky part.
- Greedy algorithms require optimal local choices.
- If locally optimal choices lead to a global optimum and
the subproblems are optimal, then greed works.
- And some other times too.
References
- Greedy Algorithms, Chapter 17 in Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen, Charles Leiserson, and Ronald Rivest, MIT Press, 1999.
- Greedy Algorithms, Chapter 5 in Algorithms by Sanjoy Dasgupta, Christos Papadimitriou, and Umesh Vizirani, McGraw-Hill, 2008
