Divide and Conquer: CS 306 Lecture notes
Outline
- Using Dividing
- What Division Does
- Divide and Conquer
- Analysis
- Recursion
- Mergesort
|

|
Looking For x
unsigned ls-find(a[], n, x)
for i = 1 to n
if a[i] = x
return i
return 0
-
ls-find() does O(n) comparisons.
Quickly Looking For x
unsigned bs-find(a[], n, x)
l = 0
r = n + 1
while l < r
m = (l + r)/2
if a[m] = x
return m
if a[m] < x
l = m + 1
else
r = m
return 0
-
bs-find() does O(log n) comparisons.
Comparison
- Why is
bs-find() faster than ls-find()?
-
bs-find() does two things ls-find() doesn't:
- Divide the array in half.
- Throw half the array away.
- Which of these is more important?
- Dividing is cheap.
- Throwing away is expensive (requires ordered data).
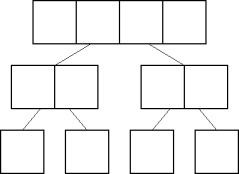
Dividing Find
unsigned d-find(a[], l, r, x)
if l + 1 = r
return a[l] = x ? l : 0
m = (l + r)/2
i = d-find(a, l, m, x)
return i == 0 ? d-find(a, m, r, x) : i
|
|
- There's not enough information to do better.
- The correct subsolution is the ultimate solution.
|
Finding Min and Max
min-max(a[], n)
min = max = a[1]
for i = 2 to n
if min > a[i]
min = a[i]
else if max < a[i]
max = a[i]
return min, max
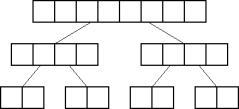
Using Dividing
min-max(a[], l, r)
if l + 2 = r
if a[l] < a[l + 1]
return a[l], a[l + 1]
else
return a[l + 1], a[l]
m = (l + r)/2
mn1, mx1 = min-max(a, l, m)
mn2, mx2 = min-max(a, m, r)
return mn1 < mn2 ? mn1 : mn2,
mx1 < mx2 ? mx2 : mx1
|
|
|
-
min-max() uses 3/2n + 1 comparisons.
|
|
What Division Does
- Division produces subproblems; each subproblem produces subsolutions.
- Subsolutions provide the information that can be exploited for
efficiency.
- The smallest subsolutions are also usually trivial to solve.
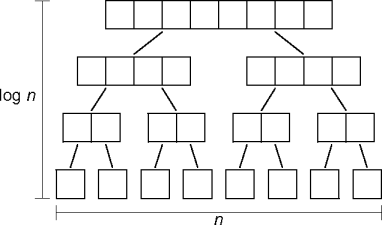
- Division also limits the subproblems to log quantities.
- Good division does, anyway.
Divide and Conquer
- The divide and conquer algorithm design technique:
- Repeatedly divide each problem into smaller subproblems.
- Solve the trivial subproblems.
- Repeatedly combine subsolutions into larger solutions.
- Divide and conquer is also the basis for other algorithm design
techniques.
Analysis
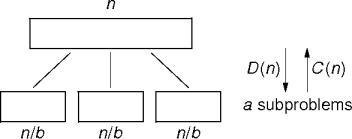
- Let T(n) be the cost of a divide-and-conquer solution on a
problem of size n. Then
| T(n) | = | aT(n/b) + D(n) + C(n) |
| or | S if n is small enough. |
Recursion
- Divide and conquer is a stylized form of recursion.
- General recursion allows arbitrary forms of subdivision.
- Divide and conquer does too, but works best when the subdivision is
uniform.
find(a[], n, x)
m = n/2
if a[m] = x
return true
if a[m] < x
return find(a + m, m, x)
return find(a, m, x)
|
find(a[], n, x)
if n = 0
return false
if a[0] = x
return true
return
find(a[1..n-1], n - 1, x)
|
Dividing to Sort
- Now recurse on the two halves.
Reuniting Divisions
- A segment of size less than two is sorted.
- Two sorted subsegments can be merged back into the original
segment.
- And the original segment will be sorted too.
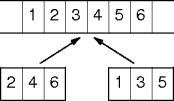
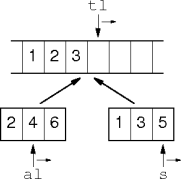
Merging
- Scan from left to right, copying the minimum value.
|
|
merge(T *
tl, tr, al, am, ar)
T * s = am
while tl < tr
if (al < am) ∧
(s == ar or *al < *s)
*tl++ = *al++
else
*tl++ = *s++
|
Mergesort
mergesort(T * aleft, aright, tleft, tright)
len = aright - aleft
if len > 1
mid = len/2
T * amid = aleft + mid
T * tmid = tleft + mid
mergesort(aleft, amid, tleft, tmid)
mergesort(amid, aright, tmid, tright)
merge(
tleft, tright, aleft, amid, aright)
Analysis
- In this case a = b = 2, D(n) = 1, C(n) = n,
and S = 1.
- Total work is O(n log n).
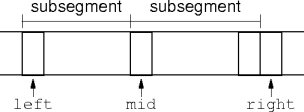
Array Merging
| 
|
The orignal data segment
|
| 
|
is split in place into halves.
|
| 
|
The subsegments occupy the segment they're supposed to merge into.
|
Array Mergesort
- Declare a second array to merge into, then copy back to the original
array.
mergesort(a[], n)
copy = new [n]
mergesort(a, a + n, copy, copy + n)
for i = 1 to n
a[i] = copy[i]
delete [] copy
-
mergesort() on arrays takes O(n) space.
Linked-List Dividing
- Linked lists can be divided with O(n) work if the list size is known.
- Walk over n/2 elements to the middle.
- What if the list size isn't known?
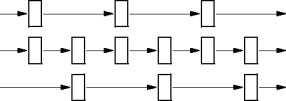
- Unzip the original list into two sublists with O(n) work.
Summary
- Divide and conquer is an algorithm design technique.
- It's also a technique to add to other designs.
- Divide and conquer is a stylized form of recursion.
- Even division into subproblems provides the best opportunity for good
performance.
- Mergesort is a guaranteed O(n log n) sort.
References
Credits










