- Three class specific problems - destructors, copying, and assignments.
- Worse than dynamic storage and exceptions; leaks o' plenty.
Compile-Time Allocation
- Use a big-enough array to hold the data.
- Grossly over-estimating the worst case size.
- It wastes space, but so what?
- Good for small amounts of data with small variability.
- The more data, the more waste.
- Highly variable data may be too big too often.
Compile-Time Problems
- Space inefficient, but implementation- and run-time efficient.
- However, run-time costs include virtual storage behavior.
- Not flexible, but safe with proper checking.
- Make sure you do the checking.
- This is a dangerous form of program design.
- Also known as pre-allocation.
Example
- Compute statistics for everyone at Monmouth.
- Assumption: the data set is small and slowly varying.
- Around 6,000 students.
- Double for the administrators - 12,000 total.
- Double it to be safe - 24,000 total.
const unsigned mu_population = 24000 static personnel_record[mu_population]
- Around 5 meg at 200 bytes/record.
An Anti-Example
- Compile-time allocation is easy to get wrong and hard to get right.
char line[100] while (cin >> line) { ... } - Poor size estimate - 100 is too small.
- No checking - input buffer overflow.
- Use
cin.getline(line, 100).
- Use
- Poor coding - the magic number 100.
- Use
const unsigned ln_size = 100.
- Use
The Example Reworked
- Adding these improvements gives
const unsigned line_size = 100 char line[line_size] while cin.getline(line, line_size) { ... }- Don't forget to handle truncated lines.
- Strings do this job easier and better.
- Compile-time allocation is easy to get wrong and hard to get right.
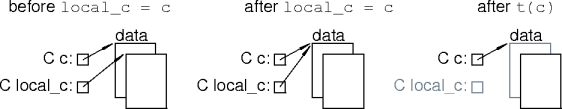
Class and Pointers
- What's wrong with this code?
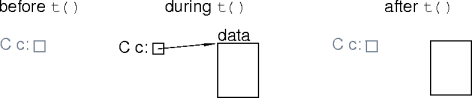
struct C {
data * data_ptr;
C() : data_ptr(new data) { }
};
static void t(void) { C c; }
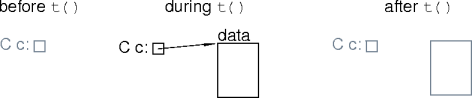
Destructors and Pointers
- If a class allocates it, the class should free it.
struct C { data * data_ptr; C() : data_ptr(new data) { } ~C() { delete data_ptr; } }; - The class destructor frees class-allocated storage.
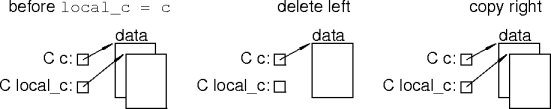
Classes and Pointers II
- What's wrong with this code?
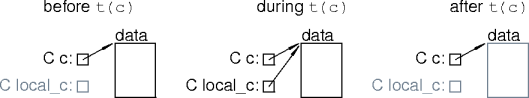
struct C {
data * data_ptr;
C() : data_ptr(new data) { }
~C() { delete data_ptr; }
};
static void t(C & c) { C local_c(c); }
Class Instance Copying
- By default, class instances are byte-wise copied.
- This replicates pointers, leading to un-intented sharing and dangling pointers on destruction.
- Class instance copying happens all the time.
- For example, non-reference class parameters.
void t(C c) {...}The call
t(c)makes a copy ofc.
- For example, non-reference class parameters.
The Copy Constructor
- A copy constructor handles dynamic-storage copying.
- The prototype is
C::C(const C &). - Don't forget the reference
&.
- The prototype is
- The details depend on the storage being managed.
- Assume internal data has copy constructors too.
Copying Data
- The copy constructor replicates data.
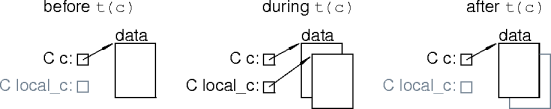
struct C {
data * data_ptr;
C() : data_ptr(new data) { }
~C() { delete data_ptr; }
C(const C & c)
: data_ptr(new data(*(c.data_ptr))) {...}
};
Classes and Pointers III
- What's wrong with this code?
struct C
data * data_ptr;
C() : data_ptr(new data) { }
~C() { delete data_ptr; }
C(const C & c)
: data_ptr(new data(*(c.data_ptr))) {...}
static void t(C & c) {C local_c; local_c = c;}
Class Instance Assignment
- Instance assignment is similar to instance copying.
- The default assignment copies byte-by-byte.
- This leads to unintended sharing, dangling pointers, and garbage.
- The previous contents of
local_c.data_ptris garbage. -
local_c.data_ptrandc.data_ptrare sharing storage.
- The previous contents of
- This leads to unintended sharing, dangling pointers, and garbage.
Assignments
- Classes should define an assignment operator to manage storage during assignments.
- Dynamic storage management in assignments involves:
- Deallocating storage in the instance to the left of the
=. - Duplicating storage from the instance to the right of the
=. - Doing the pointer assignment.
- Deallocating storage in the instance to the left of the
The Assignment Operator
struct C
data * data_ptr;
C() : data_ptr(new data) {...}
C(const C & c)
: data_ptr(new data(*c.data_ptr)) {...}
~C() { delete data_ptr; }
// Bad example.
C & operator = (const C & c) {
delete data_ptr;
data_ptr = new data(*c.data_ptr);
return *this;
}
Assignment Fine Points
- There're two fine points to keep in mind about assignments:
- Self-assignments.
- Getting self-assignments right is necessary.
- Assignments as expressions.
- Not as important, but expected behavior.
- Self-assignments.
Self Assignment
- An exprssion like
c = cis a self-assignment.- Self-assignment occurs in code, particularly with references and parameters.
- This is a source of nasty errors.
- What happens with
c = c?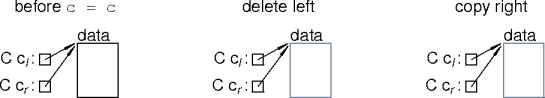
The Self-Assinment Problem
- What went wrong?
C & C::operator = (const C & rhs) { delete data_ptr; data_ptr = copy_data(rhs.data_ptr); return *this; } - Deallocating in lhs also deallocates in rhs.
- For
c = c,*this = rhs. - Deleting
data_ptrdeletesrhs.data_ptr.
- For
Handling Self-Assignment
- Make sure
*thisis different fromrhs.- If
*thisandrhsare different, proceed as normal. - If
*thisandrhsare the same, do nothing.
C & C::operator = (const C & rhs) { if (this != &rhs) { delete data_ptr; data_ptr = new data(*(rhs.data_ptr)); } return *this; } - If
Assignments as Expressions
- A little-known C++ fun fact: an assignment is an expression.
-
x = y = z = 0.0; -
if ((ch = getch()) != EOF)... - The value of an assignment is the value on the left after assignment.
-
- Overloaded assignment should support this behavior.
Assignment Prototype
- The assignment prototype
T & operator = (const T & rhs)
- The prototype can be different, but it usually shouldn't be.
- Returning a value reference should be a red flag.
- In this case, a returning a value reference is efficient and safe.
- The assignment returns
*this.
Seeming Assignments
- What's the difference between
C c2 = c1;
and
c2 = c1;
Or maybe there's no difference?
- Assignment redefines a defined instance,
copying constructing defines an undefined instance.
Assignment vs. Copying
- Despite the syntax, declared variables are initialized; the target
state is undefined.
- The alternative syntax is
C c2(c1); - Getting it wrong means unintentional replication and dangling pointers.
- The alternative syntax is
- In assignment, the target is defined and is redefined.
- Getting it wrong means unintentional replication, dangling pointers and garbage.
Assigning and Copying
- Assignment and copy constructors usually can share code.
class blob { public: ~blob() { delete(); } blob(const blob & b) { copy(b); } blob & operator = (const & blob b) { if (&b != this) { delete(); copy(b); } } private: void copy(const & blob b) {...} void delete() {...} };
The Rule of Three
- The Rule of Three:
If a class implements a destructor, a copy constructor, or an assignment operator, then it needs to implement all three.
- More simply:
A class with pointer instance variables must have a destructor, a copy constructor, and an assignment operator.
- The rule is non-symmetric, and not hard and fast.
- A destructor without a body breaks the rule.
- A virtual destructor tends to have no body.
- Either the other two may or may not imply the other two.
- Implemented for debugging or performance analysis.
- However, any class with explicit pointers must obey the rule.
Points to Remember
- Use statically allocated storage.
- But use it carefully, and well.
- Dynamic storage is not your friend.
- Learn and follow the Rule of Three.
- The troika: destructors, copy constructors, assignment.
- Assignment is tricky.
- Return value, storage management, self assignment.