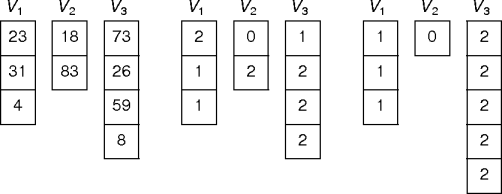

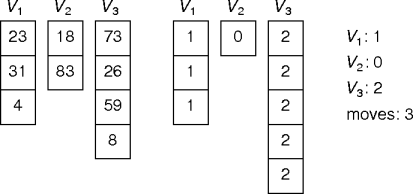
V1: 0 0 1 1 2 2 V2: 1 2 0 2 0 1 V3: 2 1 2 0 1 0
sorts[][] = { { 0, 1, 2 }, { 0, 2, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 2 }, { 1, 2, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 1 }, { 2, 1, 0 } }
sort = 0
moves = sort(v1, v2, v3, sorts[sort])
for i = 1 to 5
m = sort(v1, v2, v3, sorts[i])
if m < moves
moves = m
sort = i
return sorts[sort], moves
unsigned sort(v1[], v2[], v3[], order[])
return moves(v1, order[0]) +
moves(v2, order[1]) +
moves(v3, order[2])
unsigned moves(v[], mod)
moves = 0
for i = 1 to v.size()
if v[i] % 3 ≠ mod
moves++
return moves
sort() is O(n), where n is the total number of vector
elements,
v1.size() + v2.size() + v3.size()
int zeroMod1=0; int oneMod1=0; int twoMod1=0; int zeroMod2=0; int oneMod2=0; int twoMod2=0; int zeroMod3=0; int oneMod3=0; int twoMod3=0; int sumAll=0; int sumTotalCongruent=0; int oneSum=0; int twoSum=0; int threeSum=0; int fourSum=0; int fiveSum=0; int sixSum=0;
|
|
unsigned mod1[3] mod1[0] = mod1[1] = mod1[2] = 0 for (j = 0; j < one.size(); j++) mod1[one.at(j) % 3]++