Outline
- Abstractions and the OS.
- The five main abstractions.
- Implementing abstractions.
- Resource management.
Abstraction
- Abstraction is control over details.
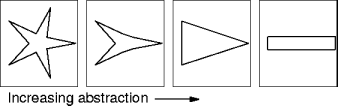
- Each level differs in the details available.
- Abstractions make complex systems understandable, implementable,
manageable.
Consider the Disk
- A magnet on a stick, a spinning magnetic disk.
- Servo-mechanisms, read-write technologies.
- Bits on a disk, addressing, errors.
- Disk interfaces.
- SCSI, IDE interfaces.
- File interfaces.
- Database interfaces.
- Web interfaces.
OS Abstractions
- An OS implements virtual machines.
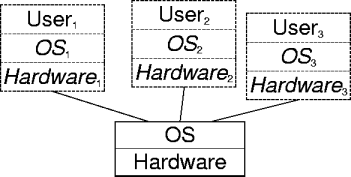
- Each virtual machine holds virtual resources for a single
real user.
Defining Abstractions
Choosing abstractions is an art and a science.
- There are different requirements on abstractions.
- The user and OS are both use abstractions.
- There are many ways of satisfying a particular point of view.
- Virtual storage (user) vs. physical storage (OS).
The Main Abstractions
- Develop an abstraction for the user.
- Develop abstractions for the resources needed by the user.
- The CPU.
- Storage of all kinds.
- Devices.
- Files.
The User Abstraction
- A user wants some computation performed.
- The computation comprises a program, and other resources too.
- A process is (almost) the set of resources required by a
computation.
- Note the difference between a process and a program.
- Processes abstract users via their computations.
The CPU Abstraction
- A process comprises almost all a computation's resources.
- The CPU is the missing resource.
- A thread abstracts CPU execution.
- A process does not own threads; threads reside in processes.
- A process executes when it has at least one resident thread.
Storage
- Cost and size; fast and small or cheap and big.
- A hierarchy of storage from fast and small to slow and huge.
- Make it all look fast and huge.
- The initial abstraction is as an array of storage units.
Devices
- Abstraction vs performance - convenience vs economy.
- Convenient abstractions are uneconomical.
- Economical abstractions are inconvenient.
- Within a device class, make them all look the same.
- What about between device classes?
Files
- File abstractions are an extension of storage.
- Persistent, nameable, gigantic storage.
- Abstractions determine naming structure and data access.
- The universal abstraction - plan 9 (and unix) treats storage
(
/dev/*mem), devices (/dev), and processes
(/dev/proc) like files.
Implementing Abstractions
- Objects are well suited for defining and implementing abstractions.
- Interfaces and encapsulation - inheritance too (subtype
polymorphism).
- Semi-natural concurrency.
- Language support.
Resource Management
- Managed for economy, protection, convenience - as always, they
conflict.
- The cycle - request, receive/deny, adjust-re-request, use, release.
This page last modified on 14 November 2004.


