Every graph has a source node and a sink node. A source node is a node with no in edges; a sink node is a node with no out edges. In the example above, node a is the source node and node d is the sink node.
For example, the graph
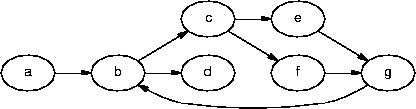
has nodes a, b, c, d, e, f, and g ; node a is the source node and node d is the sink node.
A path through a graph is a sequence of i nodes n0, n1, ... ni from the graph with the following properties:
- Node n0 is the source node.
- Nodes nk and nk + 1 for 0 <= k < i are connected by an edge.
- Node ni is the sink node.
For example, the node sequence
is a path through the graph given above, while the node sequence
is not a path for the graph above because it doesn't end at the sink node, and the node sequence
is not a path for the graph above because there is no edge between nodes g and d.
A path normally contains many redundant nodes. For example, because every path starts at the source node and ends at the sink node, it isn't really necessary to include them in the path.
A compressed path is formed by deleting redundant nodes from a path. A compressed path has the advantage of being shorter than the path from which it came, but it still has all the information necessary to reconstruct the complete path.
For example, the path
can be compressed by removing the source and sink nodes:
Notice that a compressed path usually won't be a path by the definition given above; however it's always possible to recover the proper path from the compressed path.
A minimal compressed path is a compressed path with no redundant nodes. For example, the path
produces the minimal compressed path
Note that, in general, minimal compressed paths need not be unique. For example, the path a, b, c through the graph
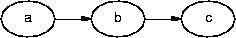
can be represented by any of the minimally compressed paths a, b, or c.