- Without recognizing the sub-linear requirement, you can't solve the problem.
- Most people failed to solve the problem.
- Anything that grows less quickly than linear growth.
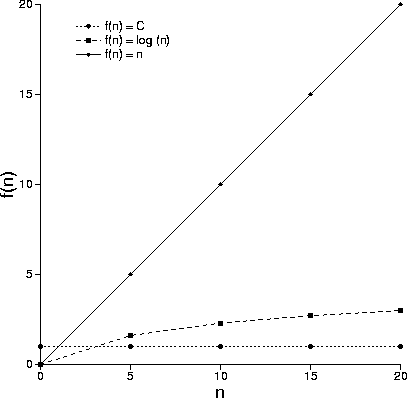
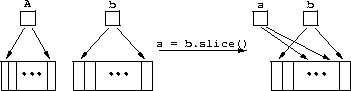
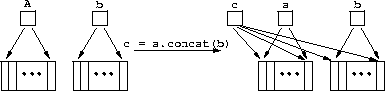
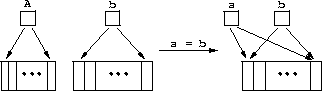
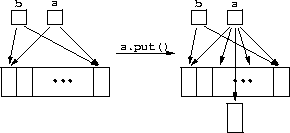
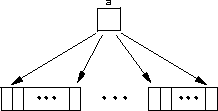
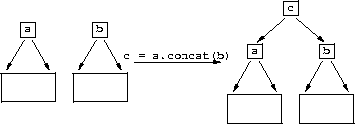
struct seq {
// The element type.
typedef int etype;
// The number of pointers.
unsigned references;
// The data stored.
const std::vector<etype> data;
}
// An empty sequence
seq() : references(0) { }
// A single-element sequence.
seq(etype e) : references(0), data(e) { }
// A range sequence.
seq(
const etype * const b,
const etype * const e)
: references(0), data(b, e) {
}
// The element count.
unsigned size(void) const
return data.size()
// Point lhs to the same thing as rhs.
friend void
seq_assign(
seq * & lhs, const seq * const rhs)
if (lhs == rhs)
return
if (lhs != 0) {
assert(lhs->references > 0)
if (--(lhs->references) == 0)
delete lhs
}
lhs = const_cast<seq *>(rhs)
if (lhs != 0)
++(lhs->references)
const trickery.
seq Member Functions
// Can't assign one sequence to another.
seq & operator = (const seq &)
return *this;
// Can't copy one sequence from another.
seq(const seq &) { }
// Can't delete a sequence.
~seq() {
assert(references == 0);
}
seq class.
seqs must come off the heap.
struct data_seq
const seq * const data;
unsigned b, e;
data_seq(const data_seq & ds)
: b(ds.b), e(ds.e)
seq_assign(const_cast(data), ds.data)
~data_seq
seq_assign(const_cast(data), 0)
unsigned size(void) const
return e - b;
b and e will differ.
This page last modified on 27 November 2002.